Create 3D Image
This example illustrates how to create a data buffer corresponding to a 3D image, and copy it in an object connectable to an ImageDev algorithm.
To invoke an ImageDev algorithm, the data to process needs to be previously imported into an ImageView object
of the IOLink library.
The first part of this example simply creates a buffer representing a 220x192x128 pixel image with a filled cube drawn inside. This step is for demonstration purposes only. In practice, you should already have the content of the image to process in a buffer stored in the data model used by your application.
Then some IOLink instructions create a new ImageView object. The buffer previously created is copied in this image with the WriteRegion method.
An ImageDev algorithm is applied afterward to show that it is now possible to process this image with ImageDev. This is the GaussianFilter3d algorithm which introduce a blur effect between the cube surface and the image background.
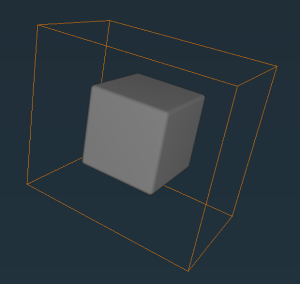
Figure 1. The 3D volume generated by this example visualized with Open Inventor
See also
The first part of this example simply creates a buffer representing a 220x192x128 pixel image with a filled cube drawn inside. This step is for demonstration purposes only. In practice, you should already have the content of the image to process in a buffer stored in the data model used by your application.
Then some IOLink instructions create a new ImageView object. The buffer previously created is copied in this image with the WriteRegion method.
An ImageDev algorithm is applied afterward to show that it is now possible to process this image with ImageDev. This is the GaussianFilter3d algorithm which introduce a blur effect between the cube surface and the image background.

Figure 1. The 3D volume generated by this example visualized with Open Inventor
#include <ImageDev/Data/ImageViewHelper.h>
#include <ImageDev/ImageDev.h>
#include <ioformat/IOFormat.h>
#include <iolink/view/ImageViewFactory.h>
#include <iolink/view/ImageViewProvider.h>
using namespace imagedev;
using namespace ioformat;
using namespace iolink;
int
main()
{
// ImageDev library initialization
if ( imagedev::isInitialized() == false )
imagedev::init();
// Initialize an unsigned 8-bit array storing data of a 3D image
const uint64_t rowCount = 220;
const uint64_t colCount = 192;
const uint64_t sliCount = 128;
std::vector< uint8_t > imageData( rowCount * colCount * sliCount );
// Define a synthetic cube in this array
const uint64_t side = colCount / 2; // side in pixels of the cube to draw
// Loop on image slices
for ( uint64_t k = 0; k < sliCount; ++k )
{
// Loop on image rows
for ( uint64_t i = 0; i < rowCount; ++i )
{
// Loop on image columns
for ( uint64_t j = 0; j < colCount; ++j )
{
if ( ( i >= ( rowCount - side ) / 2 ) && ( i <= ( rowCount + side ) / 2 ) &&
( j >= ( colCount - side ) / 2 ) && ( j <= ( colCount + side ) / 2 ) &&
( k >= ( sliCount - side ) / 2 ) && ( k <= ( sliCount + side ) / 2 ) )
imageData[k * rowCount * colCount + i * colCount + j] = 228; // Value inside the cube
else
imageData[k * rowCount * colCount + i * colCount + j] = 0; // Background value
}
}
}
// Create an image view of same dimensions
VectorXu64 imageShape{ colCount, rowCount, sliCount };
auto image = ImageViewFactory::allocate( imageShape, DataTypeId::UINT8 );
setDimensionalInterpretation( image, ImageTypeId::VOLUME );
// Define the region where to write the data
VectorXu64 imageOrig{ 0, 0, 0 };
RegionXu64 imageRegion{ imageOrig, imageShape };
// Copy the data in the image view
image->writeRegion( imageRegion, imageData.data() );
// This image can now be processed by any ImageDev algorithm, for instance for building a color image
auto imageGauss = gaussianFilter3d( image,
GaussianFilter3d::FilterMode::SEPARABLE,
{ 10.0f, 10.0f, 10.0f },
2.0f,
GaussianFilter3d::OutputType::SAME_AS_INPUT,
false );
// Save the created image with IOFormat
writeView( imageGauss, R"(T02_02_output.tif)" );
// ImageDev library finalization
imagedev::finish();
return 0;
}
using System;
using ImageDev;
using IOLink;
using IOFormat;
namespace T02_02_CreateImage3d
{
class Program
{
static void Main( string[] args )
{
// Initialize the ImageDev library if not done
if ( Initialization.IsInitialized() == false )
Initialization.Init();
// Initialize an unsigned 8-bit array storing data of a 3D image
ulong rowCount = 220;
ulong colCount = 192;
ulong sliCount = 128;
byte[] imageData = new byte[rowCount * colCount * sliCount];
// Define a synthetic cube in this array
ulong side = colCount / 2; // side in pixels of the cube to draw
// Loop on image slices
for ( ulong k = 0; k < sliCount; ++k )
{
// Loop on image rows
for ( ulong i = 0; i < rowCount; ++i )
{
// Loop on image columns
for ( ulong j = 0; j < colCount; ++j )
{
if ( ( i >= ( rowCount - side ) / 2 ) && ( i <= ( rowCount + side ) / 2 ) &&
( j >= ( colCount - side ) / 2 ) && ( j <= ( colCount + side ) / 2 ) &&
( k >= ( sliCount - side ) / 2 ) && ( k <= ( sliCount + side ) / 2 ) )
imageData[k * rowCount * colCount + i * colCount + j] = 228; // Value inside the cube
else
imageData[k * rowCount * colCount + i * colCount + j] = 0; // Background value
}
}
}
// Create an image view of same dimensions
VectorXu64 imageShape = new VectorXu64( colCount, rowCount, sliCount );
ImageView image = ImageViewFactory.Allocate( imageShape, DataTypeId.UINT8 );
Data.SetDimensionalInterpretation( image, ImageTypeId.VOLUME );
// Define the region where to write the data
VectorXu64 imageOrig = new VectorXu64( 0, 0, 0 );
RegionXu64 imageRegion = new RegionXu64( imageOrig, imageShape );
// Copy the data in the image view
image.WriteRegion( imageRegion, imageData );
// This image can now be processed by any ImageDev algorithm, for instance to generate a blur effect on its
// edges
ImageView imageGauss = Processing.GaussianFilter3d( image,
GaussianFilter3d.FilterMode.SEPARABLE,
new double[] { 10.0, 10.0, 10.0 } );
// Save the created image with IOFormat
ViewIO.WriteView( imageGauss, @"T02_02_output.tif" );
Initialization.Finish();
}
}
}
import imagedev
import iolink
import ioformat
import numpy
# Initialize the ImageDev library if not done
if (imagedev.is_initialized() == False): imagedev.init()
# Initialize an unsigned 8 - bit array storing data of a 3D image
row_count = 220
col_count = 192
sli_count = 128
image_data = numpy.zeros((row_count , col_count , sli_count), numpy.uint8)
# Define a synthetic cube in this array
side = int(col_count / 2) # side in pixels of the cube to draw
image_data[int((row_count - side) / 2):int((row_count + side) / 2),
int((col_count - side) / 2):int((col_count + side) / 2),
int((sli_count - side) / 2):int((sli_count + side) / 2)] = 228
# Create an image view of same dimensions VectorXu64
image_shape = iolink.VectorXu64(col_count, row_count, sli_count)
image = iolink.ImageViewFactory.allocate(image_shape, iolink.DataTypeId_UINT8)
imagedev.set_dimensional_interpretation(image, iolink.ImageTypeId.VOLUME)
# Define the region where to write the data
image_orig = iolink.VectorXu64(0, 0, 0)
image_region = iolink.RegionXu64(image_orig, image_shape)
# Copy the data in the image view
image.write_region(image_region, image_data)
# This image can now be processed by any ImageDev algorithm, for instance to generate a blur effect on its edges
image_gauss = imagedev.gaussian_filter_3d(image, imagedev.GaussianFilter3d.FilterMode.SEPARABLE, [10.0, 10.0, 10.0])
# Save the created image with IOFormat
ioformat.write_view(image_gauss, "T02_02_output.tif")
# ImageDev library finalization
imagedev.finish() See also