RegionalMaxima
Computes the regional maxima in a grayscale image and marks them in a binary image.
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
A regional maximum $C$ is a set of connected pixels such that:
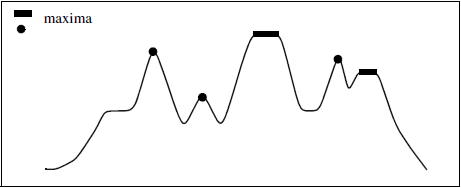
Figure 1. One-dimensional example of a regional maxima detection
This algorithm is based on [1] and uses a recursive method combined with a geodesic propagation.
To avoid getting too many regions in the output image, input should be smoothed first with a low-pass filter or with the numerical reconstruction algorithm.
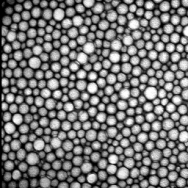
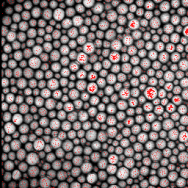
Figure 2. Original image (left) and regional maxima in red (right)
Reference:
[1] B. Laÿ. "Recursive Algorithms in Mathematical Morphology", In Acta Stereologica, vol.6/III, pp.691-696, 7th International Congress For Stereology, Caen, France, Sept. 1987.
See also
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
- section Mathematical Morphology
- section Geodesic Transformations
A regional maximum $C$ is a set of connected pixels such that:
- Pixels belonging to $C$ have the same intensity $I_C$.
- Pixels connected to $C$, but not belonging to $C$ (neighbors), have an intensity strictly lower than $I_C$.

Figure 1. One-dimensional example of a regional maxima detection
This algorithm is based on [1] and uses a recursive method combined with a geodesic propagation.
To avoid getting too many regions in the output image, input should be smoothed first with a low-pass filter or with the numerical reconstruction algorithm.
 |
 |
Reference:
[1] B. Laÿ. "Recursive Algorithms in Mathematical Morphology", In Acta Stereologica, vol.6/III, pp.691-696, 7th International Congress For Stereology, Caen, France, Sept. 1987.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns the outputBinaryImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView >
regionalMaxima( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage,
RegionalMaxima::Neighborhood neighborhood,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputBinaryImage = NULL );
This function returns the outputBinaryImage output parameter.
// Function prototype. regional_maxima( input_image, neighborhood = RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26, output_binary_image = None )
This function returns the outputBinaryImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
RegionalMaxima( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood neighborhood = ImageDev.RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26,
IOLink.ImageView outputBinaryImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Class Name | RegionalMaxima |
|---|
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr | ||||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 3D neighborhood configuration. This parameter is ignored with a 2D input image.
|
Enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_26 | |||||||
 |
outputBinaryImage |
The binary output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input. | Image | nullptr | |||||||
Object Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); RegionalMaxima regionalMaximaAlgo; regionalMaximaAlgo.setInputImage( foam ); regionalMaximaAlgo.setNeighborhood( RegionalMaxima::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 ); regionalMaximaAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << regionalMaximaAlgo.outputBinaryImage()->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
regional_maxima_algo = imagedev.RegionalMaxima()
regional_maxima_algo.input_image = foam
regional_maxima_algo.neighborhood = imagedev.RegionalMaxima.CONNECTIVITY_26
regional_maxima_algo.execute()
print( "output_binary_image:", str( regional_maxima_algo.output_binary_image ) );
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" );
RegionalMaxima regionalMaximaAlgo = new RegionalMaxima
{
inputImage = foam,
neighborhood = RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26
};
regionalMaximaAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + regionalMaximaAlgo.outputBinaryImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); auto result = regionalMaxima( foam, RegionalMaxima::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 ); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << result->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
result = imagedev.regional_maxima( foam, imagedev.RegionalMaxima.CONNECTIVITY_26 )
print( "output_binary_image:", str( result ) );
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.RegionalMaxima( foam, RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26 ); Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + result.ToString() );