VolumeProjection3d
Creates a single image containing selected pixels from a volume image.
Access to parameter description
VolumeProjection3d flattens a 3D volume into an image with only two representative dimensions.
Each output pixel is assigned by browsing a selected axis and retaining the value corresponding to a projection criterion; for example, the maximal intensity.
The output image can be considered either as a 2D image or a 3D image.
Choosing a 3D output space is almost relevant for raising ambiguity when the selected axis is not Z and the result has to be displayed in a 3D viewer.
For instance, considering that the projection is performed along X:
This map is not available in mean projection mode since, in this case, the output value is computed from all browsed intensities.
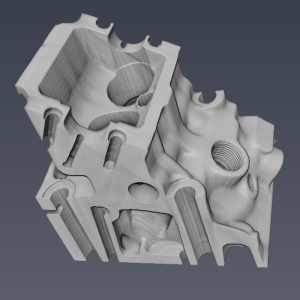
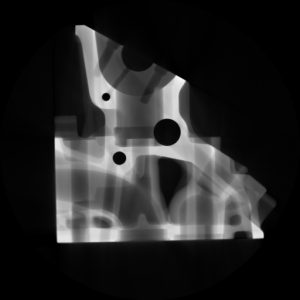
Figure 1. Mean Intensity projection: (a) The input volume,
(b) the mean projection along the Z axis, (c) mean projection along the Y axis
This algorithm is similar to ImageStackProjection3d, the main differences are:
See also
Access to parameter description
VolumeProjection3d flattens a 3D volume into an image with only two representative dimensions.
Each output pixel is assigned by browsing a selected axis and retaining the value corresponding to a projection criterion; for example, the maximal intensity.
The output image can be considered either as a 2D image or a 3D image.
Choosing a 3D output space is almost relevant for raising ambiguity when the selected axis is not Z and the result has to be displayed in a 3D viewer.
For instance, considering that the projection is performed along X:
- If the output space is 2D, the output image has two axes: X and Y. X corresponds to the Y input axis and Y to the Z input axis.
- If the output space is 3D, the output image has three axes: X, Y, and Z. The X size is 1. All axis are consistent with the input volume.
This map is not available in mean projection mode since, in this case, the output value is computed from all browsed intensities.
 (a) |
 (b) |
 (c) |
(b) the mean projection along the Z axis, (c) mean projection along the Y axis
This algorithm is similar to ImageStackProjection3d, the main differences are:
- Only the intensity minimum, maximum, and mean projection modes are available.
- The projection axis can be user-defined (X, Y, or Z) and is not necessarily the Z axis.
- The output space can be set to 3D to preserve the original coordinate system of the input volume.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns a VolumeProjection3dOutput structure containing the outputImage and outputMapImage output parameters.
// Output structure.
struct VolumeProjection3dOutput
{
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage;
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputMapImage;
};
// Function prototype.
VolumeProjection3dOutput
volumeProjection3d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage,
VolumeProjection3d::AxisDirection axisDirection,
VolumeProjection3d::ProjectionMode projectionMode,
VolumeProjection3d::DimensionalSpace dimensionalSpace,
bool createMapImage,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = NULL,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputMapImage = NULL );
This function returns a tuple containing the output_image and output_map_image output parameters.
// Function prototype.
volume_projection_3d( input_image,
axis_direction = VolumeProjection3d.AxisDirection.Z_AXIS,
projection_mode = VolumeProjection3d.ProjectionMode.INTENSITY_MEAN,
dimensional_space = VolumeProjection3d.DimensionalSpace.SPACE_2D,
create_map_image = False,
output_image = None,
output_map_image = None )
This function returns a VolumeProjection3dOutput structure containing the outputImage and outputMapImage output parameters.
/// Output structure of the VolumeProjection3d function.
public struct VolumeProjection3dOutput
{
public IOLink.ImageView outputImage;
public IOLink.ImageView outputMapImage;
};
// Function prototype.
public static VolumeProjection3dOutput
VolumeProjection3d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
VolumeProjection3d.AxisDirection axisDirection = ImageDev.VolumeProjection3d.AxisDirection.Z_AXIS,
VolumeProjection3d.ProjectionMode projectionMode = ImageDev.VolumeProjection3d.ProjectionMode.INTENSITY_MEAN,
VolumeProjection3d.DimensionalSpace dimensionalSpace = ImageDev.VolumeProjection3d.DimensionalSpace.SPACE_2D,
bool createMapImage = false,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null,
IOLink.ImageView outputMapImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Class Name | VolumeProjection3d |
|---|
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The 3D input image.
Color and grayscale images are accepted. The type of the image can be integer or float. |
Image | Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr | ||||||
 |
axisDirection |
The axis along which slices are projected.
If axis direction is set to X, YZ slices are projected.
|
Enumeration | Z_AXIS | |||||||
 |
projectionMode |
The projection criterion (the rule used to transform a stack of pixels into a single pixel).
|
Enumeration | INTENSITY_MEAN | |||||||
 |
dimensionalSpace |
Define the dimensional space of the output image.
If axis direction is set to X and space to 2D, the output X (resp. Y) axis corresponds to the Y (resp. Z) axis. If axis direction is set to X and space to 3D, the output X axis is one pixel thick.
|
Enumeration | SPACE_2D | |||||||
 |
createMapImage |
This parameter indicates whether the algorithm creates an output map image.
This parameter is ignored in INTENSITY_MEAN projection mode. |
Bool | false | |||||||
 |
outputImage |
The output image representing the volume projection according to the selected criterion.
This image can be either 2D or 3D of one pixel thickness in the selected axis direction. Its type is identical to the input image. |
Image | nullptr | |||||||
 |
outputMapImage |
Output image indicating the selected plane in INTENSITY_MINIMUM or INTENSITY_MAXIMUM mode (not available in INTENSITY_MEAN mode).
The output map image can be either 2D or 3D of one pixel thickness in the selected axis direction. Its type is integer 32 bits. |
Image | nullptr | |||||||
Object Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); VolumeProjection3d volumeProjection3dAlgo; volumeProjection3dAlgo.setInputImage( foam ); volumeProjection3dAlgo.setAxisDirection( VolumeProjection3d::AxisDirection::Z_AXIS ); volumeProjection3dAlgo.setProjectionMode( VolumeProjection3d::ProjectionMode::INTENSITY_MEAN ); volumeProjection3dAlgo.setDimensionalSpace( VolumeProjection3d::DimensionalSpace::SPACE_2D ); volumeProjection3dAlgo.setCreateMapImage( false ); volumeProjection3dAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputImage:" << volumeProjection3dAlgo.outputImage()->toString(); std::cout << "outputMapImage:" << volumeProjection3dAlgo.outputMapImage()->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
volume_projection_3d_algo = imagedev.VolumeProjection3d()
volume_projection_3d_algo.input_image = foam
volume_projection_3d_algo.axis_direction = imagedev.VolumeProjection3d.Z_AXIS
volume_projection_3d_algo.projection_mode = imagedev.VolumeProjection3d.INTENSITY_MEAN
volume_projection_3d_algo.dimensional_space = imagedev.VolumeProjection3d.SPACE_2D
volume_projection_3d_algo.create_map_image = False
volume_projection_3d_algo.execute()
print( "output_image:", str( volume_projection_3d_algo.output_image ) );
print( "output_map_image:", str( volume_projection_3d_algo.output_map_image ) );
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" );
VolumeProjection3d volumeProjection3dAlgo = new VolumeProjection3d
{
inputImage = foam,
axisDirection = VolumeProjection3d.AxisDirection.Z_AXIS,
projectionMode = VolumeProjection3d.ProjectionMode.INTENSITY_MEAN,
dimensionalSpace = VolumeProjection3d.DimensionalSpace.SPACE_2D,
createMapImage = false
};
volumeProjection3dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + volumeProjection3dAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine( "outputMapImage:" + volumeProjection3dAlgo.outputMapImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); auto result = volumeProjection3d( foam, VolumeProjection3d::AxisDirection::Z_AXIS, VolumeProjection3d::ProjectionMode::INTENSITY_MEAN, VolumeProjection3d::DimensionalSpace::SPACE_2D, false ); std::cout << "outputImage:" << result.outputImage->toString(); std::cout << "outputMapImage:" << result.outputMapImage->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
result_output_image, result_output_map_image = imagedev.volume_projection_3d( foam, imagedev.VolumeProjection3d.Z_AXIS, imagedev.VolumeProjection3d.INTENSITY_MEAN, imagedev.VolumeProjection3d.SPACE_2D, False )
print( "output_image:", str( result_output_image ) );
print( "output_map_image:", str( result_output_map_image ) );
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" ); Processing.VolumeProjection3dOutput result = Processing.VolumeProjection3d( foam, VolumeProjection3d.AxisDirection.Z_AXIS, VolumeProjection3d.ProjectionMode.INTENSITY_MEAN, VolumeProjection3d.DimensionalSpace.SPACE_2D, false ); Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.outputImage.ToString() ); Console.WriteLine( "outputMapImage:" + result.outputMapImage.ToString() );