ClosingByReconstruction2d
Performs a two-dimensional closing by reconstruction with a structuring element matching with a square.
Access to parameter description
A closing by reconstruction consists in applying a dilation followed by a morphological reconstruction. In the binary case, closing by reconstruction can be used for filling small holes without modifying edges of the large ones. In the grayscale case, opening by reconstruction can be used for performing a Top Hat by reconstruction for detecting dark small structures without getting artifacts from the boundary concavities of large structures.
Figure 1. Top Hat using closing by reconstruction: (a) Grayscale CT image with simulated
porosities,
(b) porosity detection with a classic top-hat, (c) porosity detection with a top-hat by reconstruction
See also
Access to parameter description
A closing by reconstruction consists in applying a dilation followed by a morphological reconstruction. In the binary case, closing by reconstruction can be used for filling small holes without modifying edges of the large ones. In the grayscale case, opening by reconstruction can be used for performing a Top Hat by reconstruction for detecting dark small structures without getting artifacts from the boundary concavities of large structures.
 (a) |
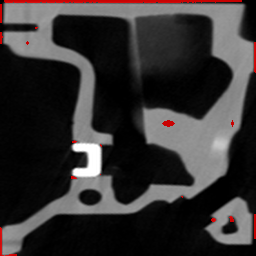 (b) |
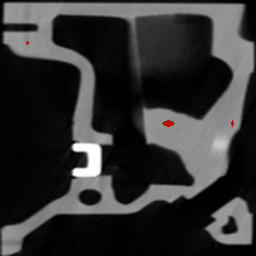 (c) |
(b) porosity detection with a classic top-hat, (c) porosity detection with a top-hat by reconstruction
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns the outputImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView >
closingByReconstruction2d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage,
uint32_t kernelRadius,
ClosingByReconstruction2d::Neighborhood neighborhood,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = NULL );
This function returns the outputImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
closing_by_reconstruction_2d( input_image,
kernel_radius = 3,
neighborhood = ClosingByReconstruction2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8,
output_image = None )
This function returns the outputImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
ClosingByReconstruction2d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
UInt32 kernelRadius = 3,
ClosingByReconstruction2d.Neighborhood neighborhood = ImageDev.ClosingByReconstruction2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Class Name | ClosingByReconstruction2d |
|---|
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. | Image | Binary, Label or Grayscale | nullptr | ||||
 |
kernelRadius |
The number of iterations (the half size of the structuring element, in pixels). A square structuring element always has an odd side length (3x3, 5x5, etc.) which is defined by twice the kernel radius + 1. | UInt32 | >=1 | 3 | ||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 2D neighborhood configuration for performing dilations or erosions.
|
Enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_8 | |||||
 |
outputImage |
The output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input image. | Image | nullptr | |||||
Object Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); ClosingByReconstruction2d closingByReconstruction2dAlgo; closingByReconstruction2dAlgo.setInputImage( polystyrene ); closingByReconstruction2dAlgo.setKernelRadius( 3 ); closingByReconstruction2dAlgo.setNeighborhood( ClosingByReconstruction2d::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_8 ); closingByReconstruction2dAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputImage:" << closingByReconstruction2dAlgo.outputImage()->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
closing_by_reconstruction_2d_algo = imagedev.ClosingByReconstruction2d()
closing_by_reconstruction_2d_algo.input_image = polystyrene
closing_by_reconstruction_2d_algo.kernel_radius = 3
closing_by_reconstruction_2d_algo.neighborhood = imagedev.ClosingByReconstruction2d.CONNECTIVITY_8
closing_by_reconstruction_2d_algo.execute()
print( "output_image:", str( closing_by_reconstruction_2d_algo.output_image ) );
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
ClosingByReconstruction2d closingByReconstruction2dAlgo = new ClosingByReconstruction2d
{
inputImage = polystyrene,
kernelRadius = 3,
neighborhood = ClosingByReconstruction2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8
};
closingByReconstruction2dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + closingByReconstruction2dAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); auto result = closingByReconstruction2d( polystyrene, 3, ClosingByReconstruction2d::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_8 ); std::cout << "outputImage:" << result->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
result = imagedev.closing_by_reconstruction_2d( polystyrene, 3, imagedev.ClosingByReconstruction2d.CONNECTIVITY_8 )
print( "output_image:", str( result ) );
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.ClosingByReconstruction2d( polystyrene, 3, ClosingByReconstruction2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8 ); Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.ToString() );