ImageStackProjection3d
Transforms a volume that represents a stack of 2D images into a single 2D image.
Access to parameter description
ImageStackProjection3d creates a single image containing pixels transformed from a stack of input images according to a user-defined projection criterion.
The ImageStackProjection3d algorithm can then be used to examine all images of this stack and retain the pixel presenting the best contrast to build the resulting image.
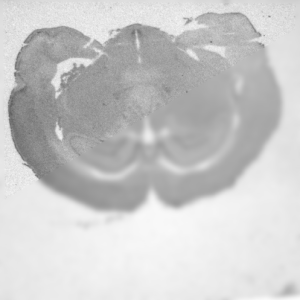
Figure 1. Z-stack projection on a two images stack: (a) first image of the stack,
(b) second image of the stack,
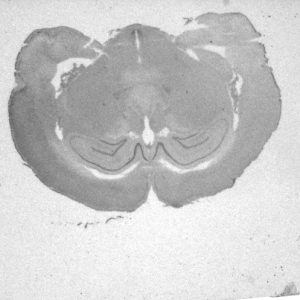
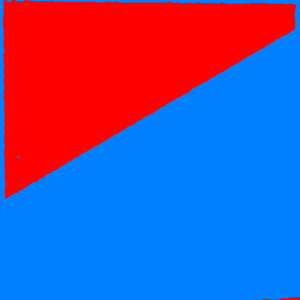
(c) gradient maxima projection, (d) pixel selection map (blue: from first image, red: from second image)
Other criteria cannot be applied on color image stacks, an exception is returned in this case.
See also
Access to parameter description
ImageStackProjection3d creates a single image containing pixels transformed from a stack of input images according to a user-defined projection criterion.
The gradient maxima projection, also known as z-stack algorithm
When acquiring a scene that is not orthogonal to the optical path (that is, not parallel to the sensor), it is generally not possible to directly get an image focused over the whole field. Nevertheless, it is possible to acquire several images of this scene, each one focused on a different region of the scene.The ImageStackProjection3d algorithm can then be used to examine all images of this stack and retain the pixel presenting the best contrast to build the resulting image.
Other pixel selection criteria
This algorithm also offers some basic selection criteria, such as intensity minimum or maximum. For instance, selecting the maximum intensity on a CT data set can be a way to simulate a classical projection radiography.Projection maps
When the projection mode is selective, like the intensity minima, maxima, or the gradient maxima, the algorithm also generates an output label image that shows the contribution source selected in the result image (the image index in the input stack).
 (a) |
 (b) |
 (c) |
 (d) |
(c) gradient maxima projection, (d) pixel selection map (blue: from first image, red: from second image)
Statistical criteria
Other criteria do not select a particular pixel from the stack, but computes each output value by performing an operation on the corresponding pixel stack. The available operators are mainly first order statistics like mean, standard deviation, energy, or entropy.Color management
When using a selective criterion on color images, the input is converted to the HSL color space and the criterion is evaluated on the lightness.Other criteria cannot be applied on color image stacks, an exception is returned in this case.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns a ImageStackProjection3dOutput structure containing the outputImage and outputMapImage output parameters.
// Output structure.
struct ImageStackProjection3dOutput
{
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage;
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputMapImage;
};
// Function prototype.
ImageStackProjection3dOutput
imageStackProjection3d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage,
ImageStackProjection3d::ProjectionMode projectionMode,
ImageStackProjection3d::AutoScale autoScale,
int32_t smoothingSize,
ImageStackProjection3d::GradientOperator gradientOperator,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = NULL,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputMapImage = NULL );
This function returns a tuple containing the output_image and output_map_image output parameters.
// Function prototype.
image_stack_projection_3d( input_image,
projection_mode = ImageStackProjection3d.ProjectionMode.GRADIENT_MAXIMA,
auto_scale = ImageStackProjection3d.AutoScale.YES,
smoothing_size = 5,
gradient_operator = ImageStackProjection3d.GradientOperator.MORPHOLOGICAL_GRADIENT,
output_image = None,
output_map_image = None )
This function returns a ImageStackProjection3dOutput structure containing the outputImage and outputMapImage output parameters.
/// Output structure of the ImageStackProjection3d function.
public struct ImageStackProjection3dOutput
{
public IOLink.ImageView outputImage;
public IOLink.ImageView outputMapImage;
};
// Function prototype.
public static ImageStackProjection3dOutput
ImageStackProjection3d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
ImageStackProjection3d.ProjectionMode projectionMode = ImageDev.ImageStackProjection3d.ProjectionMode.GRADIENT_MAXIMA,
ImageStackProjection3d.AutoScale autoScale = ImageDev.ImageStackProjection3d.AutoScale.YES,
Int32 smoothingSize = 5,
ImageStackProjection3d.GradientOperator gradientOperator = ImageDev.ImageStackProjection3d.GradientOperator.MORPHOLOGICAL_GRADIENT,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null,
IOLink.ImageView outputMapImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Class Name | ImageStackProjection3d |
|---|
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
A 3D volume representing a stack of 2D images. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr | ||||||||||||||||||
 |
projectionMode |
The projection criterion (the rule used to transform a stack of pixels into a single pixel).
|
Enumeration | GRADIENT_MAXIMA | |||||||||||||||||||
 |
autoScale |
The automatic intensity scaling mode to average the pixels of the stack. It is used only with the PROJECTION mode and is ignored with any other criterion.
|
Enumeration | YES | |||||||||||||||||||
 |
smoothingSize |
The kernel size for smoothing the gradient before selecting the output value. It is used only with the GRADIENT_MAXIMA mode and is ignored with any other criterion. | Int32 | >=0 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
 |
gradientOperator |
The gradient operator to apply.It is used only with the GRADIENT_MAXIMA mode and is ignored with any other criterion.
|
Enumeration | MORPHOLOGICAL_GRADIENT | |||||||||||||||||||
 |
outputImage |
The output image representing the volume projection according to the selected criterion. | Image | nullptr | |||||||||||||||||||
 |
outputMapImage |
The output map label image. Each pixel intensity represents the Z index used in the output image. | Image | nullptr | |||||||||||||||||||
Object Examples
auto polystyrene_seq = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene_seq.vip" ); ImageStackProjection3d imageStackProjection3dAlgo; imageStackProjection3dAlgo.setInputImage( polystyrene_seq ); imageStackProjection3dAlgo.setProjectionMode( ImageStackProjection3d::ProjectionMode::GRADIENT_MAXIMA ); imageStackProjection3dAlgo.setAutoScale( ImageStackProjection3d::AutoScale::YES ); imageStackProjection3dAlgo.setSmoothingSize( 5 ); imageStackProjection3dAlgo.setGradientOperator( ImageStackProjection3d::GradientOperator::GAUSSIAN_GRADIENT ); imageStackProjection3dAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputImage:" << imageStackProjection3dAlgo.outputImage()->toString(); std::cout << "outputMapImage:" << imageStackProjection3dAlgo.outputMapImage()->toString();
polystyrene_seq = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene_seq.vip"))
image_stack_projection_3d_algo = imagedev.ImageStackProjection3d()
image_stack_projection_3d_algo.input_image = polystyrene_seq
image_stack_projection_3d_algo.projection_mode = imagedev.ImageStackProjection3d.GRADIENT_MAXIMA
image_stack_projection_3d_algo.auto_scale = imagedev.ImageStackProjection3d.YES
image_stack_projection_3d_algo.smoothing_size = 5
image_stack_projection_3d_algo.gradient_operator = imagedev.ImageStackProjection3d.GAUSSIAN_GRADIENT
image_stack_projection_3d_algo.execute()
print( "output_image:", str( image_stack_projection_3d_algo.output_image ) );
print( "output_map_image:", str( image_stack_projection_3d_algo.output_map_image ) );
ImageView polystyrene_seq = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene_seq.vip" );
ImageStackProjection3d imageStackProjection3dAlgo = new ImageStackProjection3d
{
inputImage = polystyrene_seq,
projectionMode = ImageStackProjection3d.ProjectionMode.GRADIENT_MAXIMA,
autoScale = ImageStackProjection3d.AutoScale.YES,
smoothingSize = 5,
gradientOperator = ImageStackProjection3d.GradientOperator.GAUSSIAN_GRADIENT
};
imageStackProjection3dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + imageStackProjection3dAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine( "outputMapImage:" + imageStackProjection3dAlgo.outputMapImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
auto polystyrene_seq = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene_seq.vip" ); auto result = imageStackProjection3d( polystyrene_seq, ImageStackProjection3d::ProjectionMode::GRADIENT_MAXIMA, ImageStackProjection3d::AutoScale::YES, 5, ImageStackProjection3d::GradientOperator::GAUSSIAN_GRADIENT ); std::cout << "outputImage:" << result.outputImage->toString(); std::cout << "outputMapImage:" << result.outputMapImage->toString();
polystyrene_seq = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene_seq.vip"))
result_output_image, result_output_map_image = imagedev.image_stack_projection_3d( polystyrene_seq, imagedev.ImageStackProjection3d.GRADIENT_MAXIMA, imagedev.ImageStackProjection3d.YES, 5, imagedev.ImageStackProjection3d.GAUSSIAN_GRADIENT )
print( "output_image:", str( result_output_image ) );
print( "output_map_image:", str( result_output_map_image ) );
ImageView polystyrene_seq = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene_seq.vip" ); Processing.ImageStackProjection3dOutput result = Processing.ImageStackProjection3d( polystyrene_seq, ImageStackProjection3d.ProjectionMode.GRADIENT_MAXIMA, ImageStackProjection3d.AutoScale.YES, 5, ImageStackProjection3d.GradientOperator.GAUSSIAN_GRADIENT ); Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.outputImage.ToString() ); Console.WriteLine( "outputMapImage:" + result.outputMapImage.ToString() );