HMaxima
Merges the regional maxima in a grayscale image and marks them in a binary image.
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
The input is subtracted from the contrast coefficient $h$, then a grayscale reconstruction is performed on the result of this subtraction.
The regional maxima of the reconstructed image are called the h-maxima.
The algorithm only works with homogeneous gray level objects. The appropriate $h$ value depends on the local contrast between the gray level objects to detect. Increasing this factor too much may eliminate some previously merged objects.
This algorithm is useful for filtering noisy maxima sets.
It also can be used as particle markers in various algorithms; for example, watershed detection.
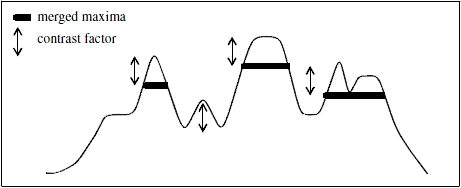
Figure 1. One-dimensional example of a reconstruction by dilation
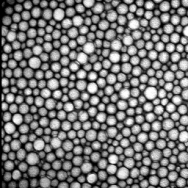
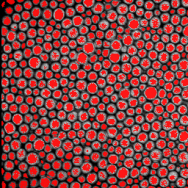
Figure 2. Original image (left) and merged maxima in red (right, contrast=60).
Reference:
P. Soille, Morphological Image Analysis. Principles and Applications, Second Edition, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp.203-204, 2003.
See also
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
- section Mathematical Morphology
- section Geodesic Transformations
The input is subtracted from the contrast coefficient $h$, then a grayscale reconstruction is performed on the result of this subtraction.
The regional maxima of the reconstructed image are called the h-maxima.
The algorithm only works with homogeneous gray level objects. The appropriate $h$ value depends on the local contrast between the gray level objects to detect. Increasing this factor too much may eliminate some previously merged objects.
This algorithm is useful for filtering noisy maxima sets.
It also can be used as particle markers in various algorithms; for example, watershed detection.

Figure 1. One-dimensional example of a reconstruction by dilation
 |
 |
Reference:
P. Soille, Morphological Image Analysis. Principles and Applications, Second Edition, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp.203-204, 2003.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns the outputBinaryImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView >
hMaxima( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage,
int32_t contrast,
HMaxima::Neighborhood neighborhood,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputBinaryImage = NULL );
This function returns the outputBinaryImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
h_maxima( input_image,
contrast = 4,
neighborhood = HMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26,
output_binary_image = None )
This function returns the outputBinaryImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
HMaxima( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
Int32 contrast = 4,
HMaxima.Neighborhood neighborhood = ImageDev.HMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26,
IOLink.ImageView outputBinaryImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Class Name | HMaxima |
|---|
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The grayscale input image. | Image | Grayscale | nullptr | ||||||
 |
contrast |
The contrast level h. | Int32 | Any value | 4 | ||||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 3D neighborhood configuration. This parameter is ignored with a 2D input image.
|
Enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_26 | |||||||
 |
outputBinaryImage |
The binary output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input. | Image | nullptr | |||||||
Object Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); HMaxima hMaximaAlgo; hMaximaAlgo.setInputImage( foam ); hMaximaAlgo.setContrast( 4 ); hMaximaAlgo.setNeighborhood( HMaxima::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 ); hMaximaAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << hMaximaAlgo.outputBinaryImage()->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
h_maxima_algo = imagedev.HMaxima()
h_maxima_algo.input_image = foam
h_maxima_algo.contrast = 4
h_maxima_algo.neighborhood = imagedev.HMaxima.CONNECTIVITY_26
h_maxima_algo.execute()
print( "output_binary_image:", str( h_maxima_algo.output_binary_image ) );
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" );
HMaxima hMaximaAlgo = new HMaxima
{
inputImage = foam,
contrast = 4,
neighborhood = HMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26
};
hMaximaAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + hMaximaAlgo.outputBinaryImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); auto result = hMaxima( foam, 4, HMaxima::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 ); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << result->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
result = imagedev.h_maxima( foam, 4, imagedev.HMaxima.CONNECTIVITY_26 )
print( "output_binary_image:", str( result ) );
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.HMaxima( foam, 4, HMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26 ); Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + result.ToString() );