UnsharpMasking2d
Sharpens edges on the elements of a two-dimensional image without increasing noise.
Access to parameter description
For an introduction to image filters: see section Images Filtering.
This algorithm is a very common filter that sharpens edges on the elements of an image without increasing noise. It first applies a Gaussian gradient and merges the result with the original image. Undesired effects are finally reduced by using a mask to apply the sharpening only on the desired regions (that is, regions for which the gradient is above a certain threshold). $$ O=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} I + (I - G_\sigma) \times amount & \mbox {if $G_\sigma \geq T$} \\ I & \mbox{otherwise} \end{array}\right. $$ Where:
Figure 1. The unsharp masking filter effect: (a) the orginal image,
(b) unsharp masking with $\sigma=1$, $ amount=7$, and $T=0$, (c) same processing with $T=90$
Note: Since the original data range is not preserved by this filter, the output image type is upgraded according to the Image type basic rule.
Reference:
R.C. Gonzalez, R.E. Woods, Digital Image Processing, Third Edition, Pearson, New Jersey, pp.184-187, 2010.
See also
Access to parameter description
For an introduction to image filters: see section Images Filtering.
This algorithm is a very common filter that sharpens edges on the elements of an image without increasing noise. It first applies a Gaussian gradient and merges the result with the original image. Undesired effects are finally reduced by using a mask to apply the sharpening only on the desired regions (that is, regions for which the gradient is above a certain threshold). $$ O=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} I + (I - G_\sigma) \times amount & \mbox {if $G_\sigma \geq T$} \\ I & \mbox{otherwise} \end{array}\right. $$ Where:
- $I$ is the input image.
- $G_\sigma$ is the Gaussian gradient of standard deviation $\sigma$, defined by the edgeSize parameter.
- $amount$ is the level of contrast to add. It is defined by the edgeContrast parameter.
- $T$ is the sharpening threshold. It is defined by the brightnessThreshold parameter.
- $O$ is the ouput image.
 a |
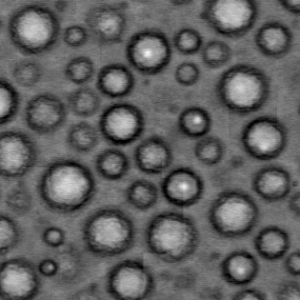 b |
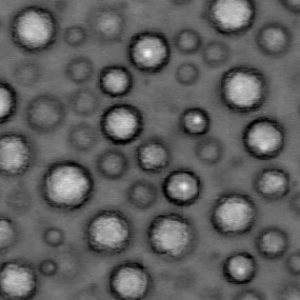 c |
(b) unsharp masking with $\sigma=1$, $ amount=7$, and $T=0$, (c) same processing with $T=90$
Note: Since the original data range is not preserved by this filter, the output image type is upgraded according to the Image type basic rule.
Reference:
R.C. Gonzalez, R.E. Woods, Digital Image Processing, Third Edition, Pearson, New Jersey, pp.184-187, 2010.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > unsharpMasking2d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage, double edgeSize, double edgeContrast, double brightnessThreshold, std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = nullptr );
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype.
unsharp_masking_2d(input_image: idt.ImageType,
edge_size: float = 5,
edge_contrast: float = 0.5,
brightness_threshold: float = 0,
output_image: idt.ImageType = None) -> idt.ImageType
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
UnsharpMasking2d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
double edgeSize = 5,
double edgeContrast = 0.5,
double brightnessThreshold = 0,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr |
 |
edgeSize |
The radius of the desired edges in pixels, used as standard deviation of the Gaussian gradient. | Float64 | >0 | 5 |
 |
edgeContrast |
The contrast amount added at the edges. | Float64 | >0 | 0.5 |
 |
brightnessThreshold |
The minimum brightness threshold. | Float64 | >=0 | 0 |
 |
outputImage |
The output image. Its dimensions are forced to the same values as the input. Its data type is promoted. | Image | nullptr | |
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
input_image |
The input image. | image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | None |
 |
edge_size |
The radius of the desired edges in pixels, used as standard deviation of the Gaussian gradient. | float64 | >0 | 5 |
 |
edge_contrast |
The contrast amount added at the edges. | float64 | >0 | 0.5 |
 |
brightness_threshold |
The minimum brightness threshold. | float64 | >=0 | 0 |
 |
output_image |
The output image. Its dimensions are forced to the same values as the input. Its data type is promoted. | image | None | |
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | null |
 |
edgeSize |
The radius of the desired edges in pixels, used as standard deviation of the Gaussian gradient. | Float64 | >0 | 5 |
 |
edgeContrast |
The contrast amount added at the edges. | Float64 | >0 | 0.5 |
 |
brightnessThreshold |
The minimum brightness threshold. | Float64 | >=0 | 0 |
 |
outputImage |
The output image. Its dimensions are forced to the same values as the input. Its data type is promoted. | Image | null | |
Object Examples
auto polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); UnsharpMasking2d unsharpMasking2dAlgo; unsharpMasking2dAlgo.setInputImage( polystyrene ); unsharpMasking2dAlgo.setEdgeSize( 5.0 ); unsharpMasking2dAlgo.setEdgeContrast( 0.5 ); unsharpMasking2dAlgo.setBrightnessThreshold( 0.0 ); unsharpMasking2dAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputImage:" << unsharpMasking2dAlgo.outputImage()->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
unsharp_masking_2d_algo = imagedev.UnsharpMasking2d()
unsharp_masking_2d_algo.input_image = polystyrene
unsharp_masking_2d_algo.edge_size = 5.0
unsharp_masking_2d_algo.edge_contrast = 0.5
unsharp_masking_2d_algo.brightness_threshold = 0.0
unsharp_masking_2d_algo.execute()
print("output_image:", str(unsharp_masking_2d_algo.output_image))
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
UnsharpMasking2d unsharpMasking2dAlgo = new UnsharpMasking2d
{
inputImage = polystyrene,
edgeSize = 5.0,
edgeContrast = 0.5,
brightnessThreshold = 0.0
};
unsharpMasking2dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + unsharpMasking2dAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
auto polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); auto result = unsharpMasking2d( polystyrene, 5.0, 0.5, 0.0 ); std::cout << "outputImage:" << result->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
result = imagedev.unsharp_masking_2d(polystyrene, 5.0, 0.5, 0.0)
print("output_image:", str(result))
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.UnsharpMasking2d( polystyrene, 5.0, 0.5, 0.0 ); Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.ToString() );
© 2025 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved.