SsimValue2d
Computes the mean structural similarity (SSIM) index between two two-dimensional images.
Access to parameter description
This algorithm provides a measure of similarity by computing the SSIM value for each pixel of the couple of image and by returning the mean of all these values.
For each pixel, we compute the SSIM value by using the following formula :
$$ SSIM(I_{1},I_{2}) = \frac{\left ( 2\mu_{1} \mu_{2} +C_{1}\right )\left ( 2\sigma_{12}+C_{2}\right )}{\left ( \mu_{1}^{2}+ \mu_{2}^{2} +C_{1}\right )\left ( \sigma_{1}^{2}+\sigma_{2}^{2}+C_{2}\right )}$$
Where:
Figure 1. Comparison of the SSIM values after adding an artificial gaussian noise of standard
deviation $\sigma$ on an original image:
(a) the reference image to compare, (b) $\sigma$=25, SSIM = 0.05 , (c) $\sigma$=80, SSIM = 0.01
Reference:
Z. Wang, A.C. Bovik, H.R. Sheikh, and E.P. Simoncelli. "Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity". IEEE Transactions on Image Processing , vol. 13, pp. 600-612, Apr. 2004.
See also
Access to parameter description
This algorithm provides a measure of similarity by computing the SSIM value for each pixel of the couple of image and by returning the mean of all these values.
For each pixel, we compute the SSIM value by using the following formula :
$$ SSIM(I_{1},I_{2}) = \frac{\left ( 2\mu_{1} \mu_{2} +C_{1}\right )\left ( 2\sigma_{12}+C_{2}\right )}{\left ( \mu_{1}^{2}+ \mu_{2}^{2} +C_{1}\right )\left ( \sigma_{1}^{2}+\sigma_{2}^{2}+C_{2}\right )}$$
Where:
- $\mu_{1}$ is the mean in the tile arround the current pixel in the image $I_{1}$,
- $\mu_{2}$ is the mean in the tile arround the current pixel in the image $I_{2}$,
- $\sigma_{1}$ is the standard deviation in the tile arround the current pixel in the image $I_{1}$,
- $\sigma_{2}$ is the standard deviation in the tile arround the current pixel in the image $I_{2}$,
- $\sigma_{12}$ is the covariance in the tile arround the current pixel in each image $I_{1}$ and $I_{2}$
- $C_{1}$ is a constant computed with the choosen range $R$ and the parameter $k_{1}$ as follow : $C_{1} = \left ( k_{1}R \right )^{2}$
- $C_{2}$ is a constant computed with the choosen range $R$ and the parameter $k_{2}$ as follow : $C_{2} = \left ( k_{2}R \right )^{2}$
 (a) |
 (b) |
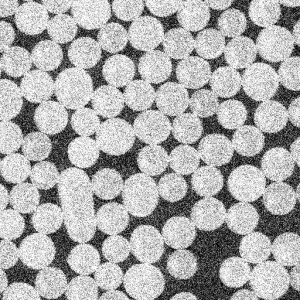 (c) |
(a) the reference image to compare, (b) $\sigma$=25, SSIM = 0.05 , (c) $\sigma$=80, SSIM = 0.01
Reference:
Z. Wang, A.C. Bovik, H.R. Sheikh, and E.P. Simoncelli. "Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity". IEEE Transactions on Image Processing , vol. 13, pp. 600-612, Apr. 2004.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns outputMeasurement.
// Function prototype
SsimValueMsr::Ptr ssimValue2d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage1, std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage2, const iolink::Vector2u32& tileSize, SsimValue2d::RangeMode rangeMode, double range, double k1, double k2, SsimValueMsr::Ptr outputMeasurement = nullptr );
This function returns outputMeasurement.
// Function prototype.
ssim_value_2d(input_image1: idt.ImageType,
input_image2: idt.ImageType,
tile_size: Iterable[int] = [8, 8],
range_mode: SsimValue2d.RangeMode = SsimValue2d.RangeMode.DATA_TYPE_RANGE,
range: float = 255,
k1: float = 0.01,
k2: float = 0.03,
output_measurement: Union[Any, None] = None) -> SsimValueMsr
This function returns outputMeasurement.
// Function prototype.
public static SsimValueMsr
SsimValue2d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage1,
IOLink.ImageView inputImage2,
uint[] tileSize = null,
SsimValue2d.RangeMode rangeMode = ImageDev.SsimValue2d.RangeMode.DATA_TYPE_RANGE,
double range = 255,
double k1 = 0.01,
double k2 = 0.03,
SsimValueMsr outputMeasurement = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage1 |
The first input image to compare. | Image | Grayscale | nullptr | ||||
 |
inputImage2 |
The second input image to compare. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr | ||||
 |
tileSize |
The X and Y sizes, in pixels, of the tile used to compute the SSIM for each pixel | Vector2u32 | >=1 | {8, 8} | ||||
 |
rangeMode |
The way to consider the dynamic range used to compute the regularization constants C1 and C2 of the similarity formula.
|
Enumeration | DATA_TYPE_RANGE | |||||
 |
range |
The data range used to compute the constants C1 and C2 of the similarity formula. It corresponds to the distance between the maximum and minimum of the representative image intensities. It is used only if rangeMode parameter is set to OTHER value. | Float64 | >0 | 255 | ||||
 |
k1 |
The small weight used to compute the regularization constant C1 of the similarity formula. | Float64 | >0 | 0.01 | ||||
 |
k2 |
The small weight used to compute the regularization constant C2 of the similarity formula. | Float64 | >0 | 0.03 | ||||
 |
outputMeasurement |
The output measurement results containing the SSIM value. | SsimValueMsr | nullptr | |||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
input_image1 |
The first input image to compare. | image | Grayscale | None | ||||
 |
input_image2 |
The second input image to compare. | image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | None | ||||
 |
tile_size |
The X and Y sizes, in pixels, of the tile used to compute the SSIM for each pixel | vector2u32 | >=1 | [8, 8] | ||||
 |
range_mode |
The way to consider the dynamic range used to compute the regularization constants C1 and C2 of the similarity formula.
|
enumeration | DATA_TYPE_RANGE | |||||
 |
range |
The data range used to compute the constants C1 and C2 of the similarity formula. It corresponds to the distance between the maximum and minimum of the representative image intensities. It is used only if rangeMode parameter is set to OTHER value. | float64 | >0 | 255 | ||||
 |
k1 |
The small weight used to compute the regularization constant C1 of the similarity formula. | float64 | >0 | 0.01 | ||||
 |
k2 |
The small weight used to compute the regularization constant C2 of the similarity formula. | float64 | >0 | 0.03 | ||||
 |
output_measurement |
The output measurement results containing the SSIM value. | SsimValueMsr | None | |||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage1 |
The first input image to compare. | Image | Grayscale | null | ||||
 |
inputImage2 |
The second input image to compare. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | null | ||||
 |
tileSize |
The X and Y sizes, in pixels, of the tile used to compute the SSIM for each pixel | Vector2u32 | >=1 | {8, 8} | ||||
 |
rangeMode |
The way to consider the dynamic range used to compute the regularization constants C1 and C2 of the similarity formula.
|
Enumeration | DATA_TYPE_RANGE | |||||
 |
range |
The data range used to compute the constants C1 and C2 of the similarity formula. It corresponds to the distance between the maximum and minimum of the representative image intensities. It is used only if rangeMode parameter is set to OTHER value. | Float64 | >0 | 255 | ||||
 |
k1 |
The small weight used to compute the regularization constant C1 of the similarity formula. | Float64 | >0 | 0.01 | ||||
 |
k2 |
The small weight used to compute the regularization constant C2 of the similarity formula. | Float64 | >0 | 0.03 | ||||
 |
outputMeasurement |
The output measurement results containing the SSIM value. | SsimValueMsr | null | |||||
Object Examples
auto polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" );
auto polystyrene_gaussian_noise = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene_gaussian_noise.vip" );
SsimValue2d ssimValue2dAlgo;
ssimValue2dAlgo.setInputImage1( polystyrene );
ssimValue2dAlgo.setInputImage2( polystyrene_gaussian_noise );
ssimValue2dAlgo.setTileSize( {8, 8} );
ssimValue2dAlgo.setRangeMode( SsimValue2d::RangeMode::DATA_TYPE_RANGE );
ssimValue2dAlgo.setRange( 255 );
ssimValue2dAlgo.setK1( 0.01 );
ssimValue2dAlgo.setK2( 0.03 );
ssimValue2dAlgo.execute();
std::cout << "ssim: " << ssimValue2dAlgo.outputMeasurement()->ssim( 0 ) ;
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
polystyrene_gaussian_noise = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene_gaussian_noise.vip"))
ssim_value_2d_algo = imagedev.SsimValue2d()
ssim_value_2d_algo.input_image1 = polystyrene
ssim_value_2d_algo.input_image2 = polystyrene_gaussian_noise
ssim_value_2d_algo.tile_size = [8, 8]
ssim_value_2d_algo.range_mode = imagedev.SsimValue2d.DATA_TYPE_RANGE
ssim_value_2d_algo.range = 255
ssim_value_2d_algo.k1 = 0.01
ssim_value_2d_algo.k2 = 0.03
ssim_value_2d_algo.execute()
print("ssim: ", str(ssim_value_2d_algo.output_measurement.ssim(0)))
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
ImageView polystyrene_gaussian_noise = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene_gaussian_noise.vip" );
SsimValue2d ssimValue2dAlgo = new SsimValue2d
{
inputImage1 = polystyrene,
inputImage2 = polystyrene_gaussian_noise,
tileSize = new uint[]{8, 8},
rangeMode = SsimValue2d.RangeMode.DATA_TYPE_RANGE,
range = 255,
k1 = 0.01,
k2 = 0.03
};
ssimValue2dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "ssim: " + ssimValue2dAlgo.outputMeasurement.ssim( 0 ) );
Function Examples
auto polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" );
auto polystyrene_gaussian_noise = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene_gaussian_noise.vip" );
auto result = ssimValue2d( polystyrene, polystyrene_gaussian_noise, {8, 8}, SsimValue2d::RangeMode::DATA_TYPE_RANGE, 255, 0.01, 0.03 );
std::cout << "ssim: " << result->ssim( 0 ) ;
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
polystyrene_gaussian_noise = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene_gaussian_noise.vip"))
result = imagedev.ssim_value_2d(polystyrene, polystyrene_gaussian_noise, [8, 8], imagedev.SsimValue2d.DATA_TYPE_RANGE, 255, 0.01, 0.03)
print("ssim: ", str(result.ssim(0)))
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
ImageView polystyrene_gaussian_noise = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene_gaussian_noise.vip" );
SsimValueMsr result = Processing.SsimValue2d( polystyrene, polystyrene_gaussian_noise, new uint[]{8, 8}, SsimValue2d.RangeMode.DATA_TYPE_RANGE, 255, 0.01, 0.03 );
Console.WriteLine( "ssim: " + result.ssim( 0 ) );
© 2025 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved.