InfluenceZones
Computes the Skeleton by Influence Zone (SKIZ).
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
The influence zone of a particle $X_i$ is the set of points closer to $X_i$ than to any other particle $X_j$.
The skeleton by influence zones is the boundary splitting the different influence zones, and it separates the image into zones surrounding each object.
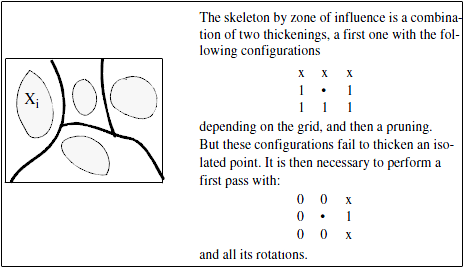
Figure 1. Skeleton by influence zones (SKIZ)
This algorithm searches the skeleton of a binary or labeled image by influence zones.
If the input is a binary image, it is first labelled, then the influence zones are determined by successive conditional dilations. $$ \begin{array}{ccc} 2 & 2 & 2\\ 1 & \bullet & 2\\ 1 & 1 & 1 \end{array} $$
The process stops as soon as all the zones are hitting each other.
See also
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
- section Mathematical Morphology
- section Skeletonization
The influence zone of a particle $X_i$ is the set of points closer to $X_i$ than to any other particle $X_j$.
The skeleton by influence zones is the boundary splitting the different influence zones, and it separates the image into zones surrounding each object.

Figure 1. Skeleton by influence zones (SKIZ)
This algorithm searches the skeleton of a binary or labeled image by influence zones.
If the input is a binary image, it is first labelled, then the influence zones are determined by successive conditional dilations. $$ \begin{array}{ccc} 2 & 2 & 2\\ 1 & \bullet & 2\\ 1 & 1 & 1 \end{array} $$
The process stops as soon as all the zones are hitting each other.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns outputBinaryImage.
// Function prototype
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > influenceZones( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputObjectImage, InfluenceZones::Neighborhood neighborhood, std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputBinaryImage = NULL );
This function returns outputBinaryImage.
// Function prototype. influence_zones( input_object_image, neighborhood = InfluenceZones.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26, output_binary_image = None )
This function returns outputBinaryImage.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
InfluenceZones( IOLink.ImageView inputObjectImage,
InfluenceZones.Neighborhood neighborhood = ImageDev.InfluenceZones.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26,
IOLink.ImageView outputBinaryImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputObjectImage |
The binary input or label image. | Image | Binary or Label | nullptr | ||||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 3D neighborhood configuration. This parameter is ignored with a 2D input image.
|
Enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_26 | |||||||
 |
outputBinaryImage |
The binary output image. Its size and type are forced to the same values as the input. | Image | nullptr | |||||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
input_object_image |
The binary input or label image. | image | Binary or Label | None | ||||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 3D neighborhood configuration. This parameter is ignored with a 2D input image.
|
enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_26 | |||||||
 |
output_binary_image |
The binary output image. Its size and type are forced to the same values as the input. | image | None | |||||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputObjectImage |
The binary input or label image. | Image | Binary or Label | null | ||||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 3D neighborhood configuration. This parameter is ignored with a 2D input image.
|
Enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_26 | |||||||
 |
outputBinaryImage |
The binary output image. Its size and type are forced to the same values as the input. | Image | null | |||||||
Object Examples
auto foam_sep = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam_sep.vip" ); InfluenceZones influenceZonesAlgo; influenceZonesAlgo.setInputObjectImage( foam_sep ); influenceZonesAlgo.setNeighborhood( InfluenceZones::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 ); influenceZonesAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << influenceZonesAlgo.outputBinaryImage()->toString();
foam_sep = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam_sep.vip"))
influence_zones_algo = imagedev.InfluenceZones()
influence_zones_algo.input_object_image = foam_sep
influence_zones_algo.neighborhood = imagedev.InfluenceZones.CONNECTIVITY_26
influence_zones_algo.execute()
print( "output_binary_image:", str( influence_zones_algo.output_binary_image ) )
ImageView foam_sep = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam_sep.vip" );
InfluenceZones influenceZonesAlgo = new InfluenceZones
{
inputObjectImage = foam_sep,
neighborhood = InfluenceZones.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26
};
influenceZonesAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + influenceZonesAlgo.outputBinaryImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
auto foam_sep = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam_sep.vip" ); auto result = influenceZones( foam_sep, InfluenceZones::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 ); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << result->toString();
foam_sep = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam_sep.vip"))
result = imagedev.influence_zones( foam_sep, imagedev.InfluenceZones.CONNECTIVITY_26 )
print( "output_binary_image:", str( result ) )
ImageView foam_sep = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam_sep.vip" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.InfluenceZones( foam_sep, InfluenceZones.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26 ); Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + result.ToString() );