RegionalMaxima
Computes the regional maxima in a grayscale image and marks them in a binary image.
Access to parameter description
This command is deprecated, it will be removed in ImageDev 2024.2.
You can use RegionalExtrema2d or RegionalExtrema3d instead.
For an introduction:
A regional maximum $C$ is a set of connected pixels such that:
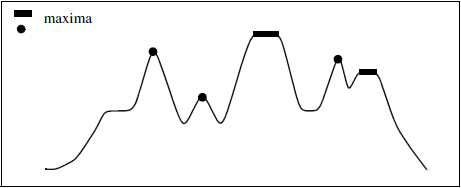
Figure 1. One-dimensional example of a regional maxima detection
This algorithm is based on [1] and uses a recursive method combined with a geodesic propagation.
To avoid getting too many regions in the output image, input should be smoothed first with a low-pass filter or with the numerical reconstruction algorithm.
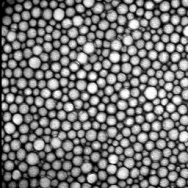
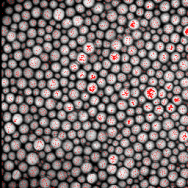
Figure 2. Original image (left) and regional maxima in red (right)
Reference:
[1] B. Laÿ. "Recursive Algorithms in Mathematical Morphology", In Acta Stereologica, vol.6/III, pp.691-696, 7th International Congress For Stereology, Caen, France, Sept. 1987.
See also
Access to parameter description
This command is deprecated, it will be removed in ImageDev 2024.2.
You can use RegionalExtrema2d or RegionalExtrema3d instead.
For an introduction:
- section Mathematical Morphology
- section Geodesic Transformations
A regional maximum $C$ is a set of connected pixels such that:
- Pixels belonging to $C$ have the same intensity $I_C$.
- Pixels connected to $C$, but not belonging to $C$ (neighbors), have an intensity strictly lower than $I_C$.

Figure 1. One-dimensional example of a regional maxima detection
This algorithm is based on [1] and uses a recursive method combined with a geodesic propagation.
To avoid getting too many regions in the output image, input should be smoothed first with a low-pass filter or with the numerical reconstruction algorithm.
 |
 |
Reference:
[1] B. Laÿ. "Recursive Algorithms in Mathematical Morphology", In Acta Stereologica, vol.6/III, pp.691-696, 7th International Congress For Stereology, Caen, France, Sept. 1987.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns outputBinaryImage.
// Function prototype
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > regionalMaxima( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage, RegionalMaxima::Neighborhood neighborhood, std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputBinaryImage = NULL );
This function returns outputBinaryImage.
// Function prototype. regional_maxima( input_image, neighborhood = RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26, output_binary_image = None )
This function returns outputBinaryImage.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
RegionalMaxima( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood neighborhood = ImageDev.RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26,
IOLink.ImageView outputBinaryImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr | ||||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 3D neighborhood configuration. This parameter is ignored with a 2D input image.
|
Enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_26 | |||||||
 |
outputBinaryImage |
The binary output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input. | Image | nullptr | |||||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
input_image |
The input image. | image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | None | ||||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 3D neighborhood configuration. This parameter is ignored with a 2D input image.
|
enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_26 | |||||||
 |
output_binary_image |
The binary output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input. | image | None | |||||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | null | ||||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 3D neighborhood configuration. This parameter is ignored with a 2D input image.
|
Enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_26 | |||||||
 |
outputBinaryImage |
The binary output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input. | Image | null | |||||||
Object Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); RegionalMaxima regionalMaximaAlgo; regionalMaximaAlgo.setInputImage( foam ); regionalMaximaAlgo.setNeighborhood( RegionalMaxima::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 ); regionalMaximaAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << regionalMaximaAlgo.outputBinaryImage()->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
regional_maxima_algo = imagedev.RegionalMaxima()
regional_maxima_algo.input_image = foam
regional_maxima_algo.neighborhood = imagedev.RegionalMaxima.CONNECTIVITY_26
regional_maxima_algo.execute()
print( "output_binary_image:", str( regional_maxima_algo.output_binary_image ) )
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" );
RegionalMaxima regionalMaximaAlgo = new RegionalMaxima
{
inputImage = foam,
neighborhood = RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26
};
regionalMaximaAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + regionalMaximaAlgo.outputBinaryImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); auto result = regionalMaxima( foam, RegionalMaxima::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 ); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << result->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
result = imagedev.regional_maxima( foam, imagedev.RegionalMaxima.CONNECTIVITY_26 )
print( "output_binary_image:", str( result ) )
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.RegionalMaxima( foam, RegionalMaxima.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_26 ); Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + result.ToString() );