ZeroCrossings2d
Thresholds pixels where the sign of a Laplacian image changes.
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
A simple zero-crossing detection is obtained by thresholding the Laplacian to retain positive intensities, then detecting the boundaries of the binary image, as shown in Figure 1. Such zero-crossing points are not precisely located.
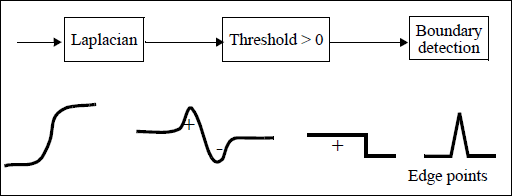
Figure 1. Thresholding a Laplacian to determine the zero-crossings
Zero-crossing is even better to mark a point if the Laplacian changes its sign in its 3x3 neighbourhood, and if the Laplacian magnitude is smaller than all magnitudes in that neighbourhood, as shown in Figure 2.
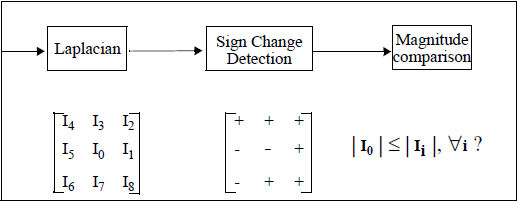
Figure 2. Zero-crossing a Laplacian
Compared to thresholding of a gradient, zero-crossings have the advantage of producing closed curves of 1 pixel thickness. This is most interesting when precise object boundary detection is the goal.
See also
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
- section Laplacian
- section Edge Marking
A simple zero-crossing detection is obtained by thresholding the Laplacian to retain positive intensities, then detecting the boundaries of the binary image, as shown in Figure 1. Such zero-crossing points are not precisely located.

Figure 1. Thresholding a Laplacian to determine the zero-crossings
Zero-crossing is even better to mark a point if the Laplacian changes its sign in its 3x3 neighbourhood, and if the Laplacian magnitude is smaller than all magnitudes in that neighbourhood, as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Zero-crossing a Laplacian
Compared to thresholding of a gradient, zero-crossings have the advantage of producing closed curves of 1 pixel thickness. This is most interesting when precise object boundary detection is the goal.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns outputBinaryImage.
// Function prototype
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > zeroCrossings2d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage, std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputBinaryImage = NULL );
This function returns outputBinaryImage.
// Function prototype. zero_crossings_2d( input_image, output_binary_image = None )
This function returns outputBinaryImage.
// Function prototype. public static IOLink.ImageView ZeroCrossings2d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage, IOLink.ImageView outputBinaryImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr |
 |
outputBinaryImage |
The binary output image. | Image | nullptr | |
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
input_image |
The input image. | image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | None |
 |
output_binary_image |
The binary output image. | image | None | |
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | null |
 |
outputBinaryImage |
The binary output image. | Image | null | |
Object Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); ZeroCrossings2d zeroCrossings2dAlgo; zeroCrossings2dAlgo.setInputImage( polystyrene ); zeroCrossings2dAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << zeroCrossings2dAlgo.outputBinaryImage()->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
zero_crossings_2d_algo = imagedev.ZeroCrossings2d()
zero_crossings_2d_algo.input_image = polystyrene
zero_crossings_2d_algo.execute()
print( "output_binary_image:", str( zero_crossings_2d_algo.output_binary_image ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
ZeroCrossings2d zeroCrossings2dAlgo = new ZeroCrossings2d
{
inputImage = polystyrene
};
zeroCrossings2dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + zeroCrossings2dAlgo.outputBinaryImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); auto result = zeroCrossings2d( polystyrene ); std::cout << "outputBinaryImage:" << result->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
result = imagedev.zero_crossings_2d( polystyrene )
print( "output_binary_image:", str( result ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.ZeroCrossings2d( polystyrene ); Console.WriteLine( "outputBinaryImage:" + result.ToString() );