MatchContrast
Computes a new image considering the dynamic range of a reference one.
Access to parameter description
This algorithm fits the dynamic range of an input image on a reference one.
The aim of this algorithm is to get an homogeneous dynamic range when processing many images, in order to be able to easily apply the same process on all of them if the intensity information is required.
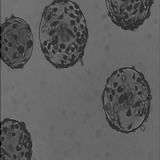
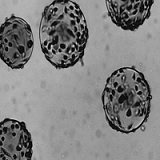
Figure 1. The Match contrast algorithm applied on similar images with different dynamic
ranges:@Br (a) the model image to dynamically register, (b) the reference image, (c) the model image
with same dynamic as the reference
There are two ways for computing the resulting image: either from the information of the reference image mean and variance, or from its histogram.
See also
Access to parameter description
This algorithm fits the dynamic range of an input image on a reference one.
The aim of this algorithm is to get an homogeneous dynamic range when processing many images, in order to be able to easily apply the same process on all of them if the intensity information is required.
 (a) |
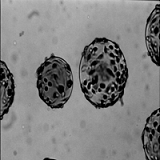 (b) |
 (c) |
There are two ways for computing the resulting image: either from the information of the reference image mean and variance, or from its histogram.
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > matchContrast( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage, std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputReferenceImage, MatchContrast::MatchingMode matchingMode, std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = NULL );
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype.
match_contrast( input_image,
input_reference_image,
matching_mode = MatchContrast.MatchingMode.MEAN_VARIANCE,
output_image = None )
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
MatchContrast( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
IOLink.ImageView inputReferenceImage,
MatchContrast.MatchingMode matchingMode = ImageDev.MatchContrast.MatchingMode.MEAN_VARIANCE,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The model input image (the image to dynamically register). | Image | Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr | ||||
 |
inputReferenceImage |
The reference image. Its type must be the same as the model. Its dimensions can be different. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr | ||||
 |
matchingMode |
The matching mode.
|
Enumeration | MEAN_VARIANCE | |||||
 |
outputImage |
The output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the model input. | Image | nullptr | |||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
input_image |
The model input image (the image to dynamically register). | image | Grayscale or Multispectral | None | ||||
 |
input_reference_image |
The reference image. Its type must be the same as the model. Its dimensions can be different. | image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | None | ||||
 |
matching_mode |
The matching mode.
|
enumeration | MEAN_VARIANCE | |||||
 |
output_image |
The output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the model input. | image | None | |||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The model input image (the image to dynamically register). | Image | Grayscale or Multispectral | null | ||||
 |
inputReferenceImage |
The reference image. Its type must be the same as the model. Its dimensions can be different. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | null | ||||
 |
matchingMode |
The matching mode.
|
Enumeration | MEAN_VARIANCE | |||||
 |
outputImage |
The output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the model input. | Image | null | |||||
Object Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); MatchContrast matchContrastAlgo; matchContrastAlgo.setInputImage( foam ); matchContrastAlgo.setInputReferenceImage( foam ); matchContrastAlgo.setMatchingMode( MatchContrast::MatchingMode::MEAN_VARIANCE ); matchContrastAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputImage:" << matchContrastAlgo.outputImage()->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
match_contrast_algo = imagedev.MatchContrast()
match_contrast_algo.input_image = foam
match_contrast_algo.input_reference_image = foam
match_contrast_algo.matching_mode = imagedev.MatchContrast.MEAN_VARIANCE
match_contrast_algo.execute()
print( "output_image:", str( match_contrast_algo.output_image ) )
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" );
MatchContrast matchContrastAlgo = new MatchContrast
{
inputImage = foam,
inputReferenceImage = foam,
matchingMode = MatchContrast.MatchingMode.MEAN_VARIANCE
};
matchContrastAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + matchContrastAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); auto result = matchContrast( foam, foam, MatchContrast::MatchingMode::MEAN_VARIANCE ); std::cout << "outputImage:" << result->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
result = imagedev.match_contrast( foam, foam, imagedev.MatchContrast.MEAN_VARIANCE )
print( "output_image:", str( result ) )
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.MatchContrast( foam, foam, MatchContrast.MatchingMode.MEAN_VARIANCE ); Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.ToString() );