CudaDilation2d
Performs a two-dimensional dilation using a structuring element matching with a square or a cross.
Access to parameter description
This command is experimental, his signature may be modified between now and his final version.
For an introduction:
This algorithm uses a basic structuring element with either 8 neighbors, or 4 neighbors, according to the neighborhood parameter.
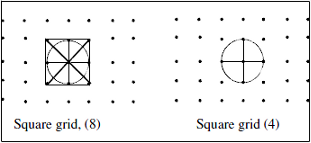
Figure 1. Structuring elements
See also
Access to parameter description
This command is experimental, his signature may be modified between now and his final version.
For an introduction:
- section Mathematical Morphology
- section Introduction To Dilation
This algorithm uses a basic structuring element with either 8 neighbors, or 4 neighbors, according to the neighborhood parameter.

Figure 1. Structuring elements
Function Syntax
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > cudaDilation2d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage, uint32_t kernelRadius, CudaDilation2d::Neighborhood neighborhood, CudaContext::Ptr cudaContext, std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = NULL );
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype.
cuda_dilation_2d( input_image,
kernel_radius = 3,
neighborhood = CudaDilation2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8,
cuda_context = None,
output_image = None )
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
CudaDilation2d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
UInt32 kernelRadius = 3,
CudaDilation2d.Neighborhood neighborhood = ImageDev.CudaDilation2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8,
Data.CudaContext cudaContext = null,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. The image type can be integer or float. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr | ||||
 |
kernelRadius |
The number of iterations (the half size of the structuring element, in pixels). A square structuring element always has an odd side length (3x3, 5x5, etc.) which is defined by twice the kernel radius + 1. | UInt32 | >=1 | 3 | ||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 2D neighborhood configuration.
|
Enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_8 | |||||
 |
cudaContext |
CUDA context information. | CudaContext | nullptr | |||||
 |
outputImage |
The output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input image. | Image | nullptr | |||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
input_image |
The input image. The image type can be integer or float. | image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | None | ||||
 |
kernel_radius |
The number of iterations (the half size of the structuring element, in pixels). A square structuring element always has an odd side length (3x3, 5x5, etc.) which is defined by twice the kernel radius + 1. | uint32 | >=1 | 3 | ||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 2D neighborhood configuration.
|
enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_8 | |||||
 |
cuda_context |
CUDA context information. | cuda_context | None | |||||
 |
output_image |
The output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input image. | image | None | |||||
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. The image type can be integer or float. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | null | ||||
 |
kernelRadius |
The number of iterations (the half size of the structuring element, in pixels). A square structuring element always has an odd side length (3x3, 5x5, etc.) which is defined by twice the kernel radius + 1. | UInt32 | >=1 | 3 | ||||
 |
neighborhood |
The 2D neighborhood configuration.
|
Enumeration | CONNECTIVITY_8 | |||||
 |
cudaContext |
CUDA context information. | CudaContext | null | |||||
 |
outputImage |
The output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input image. | Image | null | |||||
Object Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); CudaDilation2d cudaDilation2dAlgo; cudaDilation2dAlgo.setInputImage( polystyrene ); cudaDilation2dAlgo.setKernelRadius( 3 ); cudaDilation2dAlgo.setNeighborhood( CudaDilation2d::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_8 ); cudaDilation2dAlgo.setCudaContext( nullptr ); cudaDilation2dAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputImage:" << cudaDilation2dAlgo.outputImage()->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
cuda_dilation_2d_algo = imagedev.CudaDilation2d()
cuda_dilation_2d_algo.input_image = polystyrene
cuda_dilation_2d_algo.kernel_radius = 3
cuda_dilation_2d_algo.neighborhood = imagedev.CudaDilation2d.CONNECTIVITY_8
cuda_dilation_2d_algo.cuda_context = None
cuda_dilation_2d_algo.execute()
print( "output_image:", str( cuda_dilation_2d_algo.output_image ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
CudaDilation2d cudaDilation2dAlgo = new CudaDilation2d
{
inputImage = polystyrene,
kernelRadius = 3,
neighborhood = CudaDilation2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8,
cudaContext = null
};
cudaDilation2dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + cudaDilation2dAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); auto result = cudaDilation2d( polystyrene, 3, CudaDilation2d::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_8, nullptr ); std::cout << "outputImage:" << result->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
result = imagedev.cuda_dilation_2d( polystyrene, 3, imagedev.CudaDilation2d.CONNECTIVITY_8, None )
print( "output_image:", str( result ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.CudaDilation2d( polystyrene, 3, CudaDilation2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8, null ); Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.ToString() );