ErosionLine2d
Performs a two-dimensional erosion using a structuring element matching with a line.
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
The erosion is performed by using a linear structuring element. The direction of 0 degrees is horizontal and to the left, and the angles are calculated counter-clockwise.
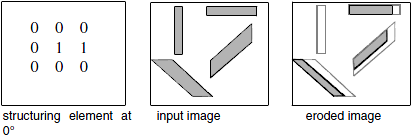
Figure 1. Linear structuring element and eroded image
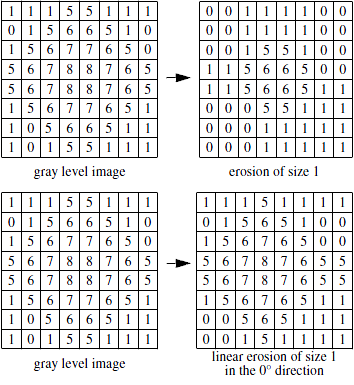
Figure 2. Two gray level erosions: by a square (top) and a linear structuring element (bottom)
See also
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
- section Mathematical Morphology
- section Introduction To Erosion
The erosion is performed by using a linear structuring element. The direction of 0 degrees is horizontal and to the left, and the angles are calculated counter-clockwise.

Figure 1. Linear structuring element and eroded image

Figure 2. Two gray level erosions: by a square (top) and a linear structuring element (bottom)
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns the outputImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView >
erosionLine2d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage,
double orientationAngle,
uint32_t kernelRadius,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = NULL );
This function returns the outputImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
erosion_line_2d( input_image,
orientation_angle = 10,
kernel_radius = 3,
output_image = None )
This function returns the outputImage output parameter.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
ErosionLine2d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
double orientationAngle = 10,
UInt32 kernelRadius = 3,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Class Name | ErosionLine2d |
|---|
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. The image type can be integer or float. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr |
 |
orientationAngle |
The angle of orientation in degrees. | Float64 | Any value | 10 |
 |
kernelRadius |
The length of the linear structuring element in pixels. | UInt32 | >=1 | 3 |
 |
outputImage |
The output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input image. | Image | nullptr | |
Object Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); ErosionLine2d erosionLine2dAlgo; erosionLine2dAlgo.setInputImage( polystyrene ); erosionLine2dAlgo.setOrientationAngle( 10 ); erosionLine2dAlgo.setKernelRadius( 3 ); erosionLine2dAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputImage:" << erosionLine2dAlgo.outputImage()->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
erosion_line_2d_algo = imagedev.ErosionLine2d()
erosion_line_2d_algo.input_image = polystyrene
erosion_line_2d_algo.orientation_angle = 10
erosion_line_2d_algo.kernel_radius = 3
erosion_line_2d_algo.execute()
print( "output_image:", str( erosion_line_2d_algo.output_image ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
ErosionLine2d erosionLine2dAlgo = new ErosionLine2d
{
inputImage = polystyrene,
orientationAngle = 10,
kernelRadius = 3
};
erosionLine2dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + erosionLine2dAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); auto result = erosionLine2d( polystyrene, 10, 3 ); std::cout << "outputImage:" << result->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
result = imagedev.erosion_line_2d( polystyrene, 10, 3 )
print( "output_image:", str( result ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.ErosionLine2d( polystyrene, 10, 3 ); Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.ToString() );