ElasticRegistration2d
Computes the optimal elastic transformation to register a two-dimensional a moving image onto a fixed image.
Access to parameter description
For an introduction: section Image Registration.
Contrary to rigid tranformations, elastic transformations warp locally the moving image to align it with the fixed image. The implementation described here relies on the demon's algorithm published by Jean-Pierre Thirion [1].
This algorithm generates two images:
The force field is an elementary displacement which is iteratively added to the current displacement field during the registration procedure. This force field tends to decrease the similarity measurement between both images.
ElasticRegistration2d also provides a multi-resolution approach which prevents the optimization procedure from falling into a local extrema and also speeds up the calculation.
The coarsest and the finest resolution levels of the multi-resolution can be user-defined. The registration is evaluated at the coarsest level first and then iteratively at each level until the finest one. The higher the finest level, the faster the computation. The lower the finest level, the more accurate the registration.
Figure 1. Elastic registration by demon's algorithm: (a) the fixed image,
(b) the moving image (artificially distorted image), (c) the moving image registered on the fixed image
This algorithm can notify some information during the processing (pyramid level, number of iterations, energy)
and can be interrupted. These information can be intercepted with the progress data callback function
defined by the setProgressDataCallback function.
In this case, data sent to the callback will be a string containing a JSON structure including
the pyramid level, the number of iterations, and the energy.
Intercepting these events slows down the execution.
More information on the callback functions can be found in the Processing interaction section.
Reference:
Access to parameter description
For an introduction: section Image Registration.
Contrary to rigid tranformations, elastic transformations warp locally the moving image to align it with the fixed image. The implementation described here relies on the demon's algorithm published by Jean-Pierre Thirion [1].
This algorithm generates two images:
- A displacement image which represents the computed transformation. Each pixel of this image contains two values: a displacement to apply in the X direction and another to apply in the Y direction on the corresponding pixel of the moving image to be registered on the fixed image.
- The result of the registration of the moving image on the fixed image.
The force field is an elementary displacement which is iteratively added to the current displacement field during the registration procedure. This force field tends to decrease the similarity measurement between both images.
ElasticRegistration2d also provides a multi-resolution approach which prevents the optimization procedure from falling into a local extrema and also speeds up the calculation.
The coarsest and the finest resolution levels of the multi-resolution can be user-defined. The registration is evaluated at the coarsest level first and then iteratively at each level until the finest one. The higher the finest level, the faster the computation. The lower the finest level, the more accurate the registration.
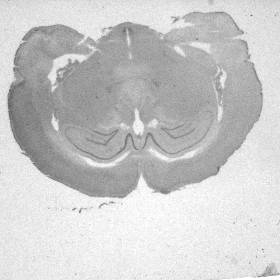 (a) |
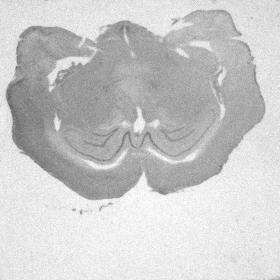 (b) |
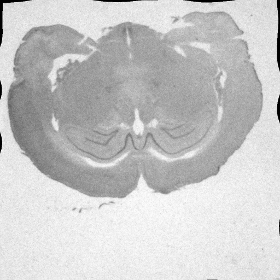 (c) |
(b) the moving image (artificially distorted image), (c) the moving image registered on the fixed image
More information on the callback functions can be found in the Processing interaction section.
Reference:
- [1] J.P.Thirion. Image matching as a diffusion process: an analogy with Maxwell s demons. Medical Image Analysis , Elsevier, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 243 260, 1998
Function Syntax
This function returns a ElasticRegistration2dOutput structure containing the outputImage and outputDisplacementField output parameters.
// Output structure.
struct ElasticRegistration2dOutput
{
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage;
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputDisplacementField;
};
// Function prototype.
ElasticRegistration2dOutput
elasticRegistration2d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputFixedImage,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputMovingImage,
ElasticRegistration2d::MetricType metricType,
double tolerance,
iolink::Vector2u32 pyramidLevels,
iolink::Vector2d elasticStandardDeviation,
iolink::Vector2d fluidStandardDeviation,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = NULL,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputDisplacementField = NULL );
This function returns a tuple containing the output_image and output_displacement_field output parameters.
// Function prototype.
elastic_registration_2d( input_fixed_image,
input_moving_image,
metric_type = ElasticRegistration2d.MetricType.MEAN_SQUARE_DIFFERENCE,
tolerance = 0.025,
pyramid_levels = [2, 0],
elastic_standard_deviation = [10, 10],
fluid_standard_deviation = [10, 10],
output_image = None,
output_displacement_field = None )
This function returns a ElasticRegistration2dOutput structure containing the outputImage and outputDisplacementField output parameters.
/// Output structure of the ElasticRegistration2d function.
public struct ElasticRegistration2dOutput
{
public IOLink.ImageView outputImage;
public IOLink.ImageView outputDisplacementField;
};
// Function prototype.
public static ElasticRegistration2dOutput
ElasticRegistration2d( IOLink.ImageView inputFixedImage,
IOLink.ImageView inputMovingImage,
ElasticRegistration2d.MetricType metricType = ImageDev.ElasticRegistration2d.MetricType.MEAN_SQUARE_DIFFERENCE,
double tolerance = 0.025,
uint[] pyramidLevels = null,
double[] elasticStandardDeviation = null,
double[] fluidStandardDeviation = null,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null,
IOLink.ImageView outputDisplacementField = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Class Name | ElasticRegistration2d |
|---|
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputFixedImage |
The input fixed grayscale image on which the moving image has to be registered. | Image | Grayscale | nullptr | ||||
 |
inputMovingImage |
The input moving grayscale image to be registered. Its dimensions and type can be different than the moving image input. | Image | Grayscale | nullptr | ||||
 |
metricType |
The type of metric used to measure the similarity/dissimilarity between the fixed and the transformed image.
|
Enumeration | MEAN_SQUARE_DIFFERENCE | |||||
 |
tolerance |
The maximum relative variation of the metric to stop the process. This variation is recomputed at each iteration. | Float64 | >0 | 0.025 | ||||
 |
pyramidLevels |
The two-dimensional vector representing the coarsest (resp. finest) resolution level in its first (resp. second) element.
A value of 0 corresponds to the full resolution and a value of $N$ corresponds to a resolution of $ \frac{1}{2^N} $. |
Vector2u32 | Any value | {2, 0} | ||||
 |
elasticStandardDeviation |
The standard deviation of the gaussian kernel used to smooth the displacement field at each iteration. | Vector2d | >0 | {10.f, 10.f} | ||||
 |
fluidStandardDeviation |
The standard deviation of the gaussian kernel used to smooth the forces field at each iteration. This parameter value is critical to reach large displacements. | Vector2d | >0 | {10.f, 10.f} | ||||
 |
outputImage |
The moving image transformed by the output displacement field. Its dimensions are forced to the same values as the fixed image, its type is forced to floating point precision (32-bit). | Image | nullptr | |||||
 |
outputDisplacementField |
The displacement field that maps a pixel of the moving image onto the corresponding pixel in the fixed image. Each pixel of the displacement image contains two values: the first one represents the displacement in the X direction and one in the Y direction. Its dimensions are forced to the same values as the moving image, and its type is forced to floating point precision (32-bit). | Image | nullptr | |||||
Object Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" );
ElasticRegistration2d elasticRegistration2dAlgo;
elasticRegistration2dAlgo.setInputFixedImage( polystyrene );
elasticRegistration2dAlgo.setInputMovingImage( polystyrene );
elasticRegistration2dAlgo.setMetricType( ElasticRegistration2d::MetricType::MEAN_SQUARE_DIFFERENCE );
elasticRegistration2dAlgo.setTolerance( 0.025 );
elasticRegistration2dAlgo.setPyramidLevels( {2, 0} );
elasticRegistration2dAlgo.setElasticStandardDeviation( {10.0, 10.0} );
elasticRegistration2dAlgo.setFluidStandardDeviation( {10.0, 10.0} );
elasticRegistration2dAlgo.execute();
std::cout << "outputImage:" << elasticRegistration2dAlgo.outputImage()->toString();
std::cout << "outputDisplacementField:" << elasticRegistration2dAlgo.outputDisplacementField()->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
elastic_registration_2d_algo = imagedev.ElasticRegistration2d()
elastic_registration_2d_algo.input_fixed_image = polystyrene
elastic_registration_2d_algo.input_moving_image = polystyrene
elastic_registration_2d_algo.metric_type = imagedev.ElasticRegistration2d.MEAN_SQUARE_DIFFERENCE
elastic_registration_2d_algo.tolerance = 0.025
elastic_registration_2d_algo.pyramid_levels = [2, 0]
elastic_registration_2d_algo.elastic_standard_deviation = [10.0, 10.0]
elastic_registration_2d_algo.fluid_standard_deviation = [10.0, 10.0]
elastic_registration_2d_algo.execute()
print( "output_image:", str( elastic_registration_2d_algo.output_image ) )
print( "output_displacement_field:", str( elastic_registration_2d_algo.output_displacement_field ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
ElasticRegistration2d elasticRegistration2dAlgo = new ElasticRegistration2d
{
inputFixedImage = polystyrene,
inputMovingImage = polystyrene,
metricType = ElasticRegistration2d.MetricType.MEAN_SQUARE_DIFFERENCE,
tolerance = 0.025,
pyramidLevels = new uint[]{2, 0},
elasticStandardDeviation = new double[]{10.0, 10.0},
fluidStandardDeviation = new double[]{10.0, 10.0}
};
elasticRegistration2dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + elasticRegistration2dAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine( "outputDisplacementField:" + elasticRegistration2dAlgo.outputDisplacementField.ToString() );
Function Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" );
auto result = elasticRegistration2d( polystyrene, polystyrene, ElasticRegistration2d::MetricType::MEAN_SQUARE_DIFFERENCE, 0.025, {2, 0}, {10.0, 10.0}, {10.0, 10.0} );
std::cout << "outputImage:" << result.outputImage->toString();
std::cout << "outputDisplacementField:" << result.outputDisplacementField->toString();
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
result_output_image, result_output_displacement_field = imagedev.elastic_registration_2d( polystyrene, polystyrene, imagedev.ElasticRegistration2d.MEAN_SQUARE_DIFFERENCE, 0.025, [2, 0], [10.0, 10.0], [10.0, 10.0] )
print( "output_image:", str( result_output_image ) )
print( "output_displacement_field:", str( result_output_displacement_field ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
Processing.ElasticRegistration2dOutput result = Processing.ElasticRegistration2d( polystyrene, polystyrene, ElasticRegistration2d.MetricType.MEAN_SQUARE_DIFFERENCE, 0.025, new uint[]{2, 0}, new double[]{10.0, 10.0}, new double[]{10.0, 10.0} );
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.outputImage.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine( "outputDisplacementField:" + result.outputDisplacementField.ToString() );