Particle Analysis
This example chains several classic image processing algorithms, and extracts features of particles contained in a grayscale image.
The first step of this example consists in binarizing the input grayscale image.
The ThresholdingByCriterion algorithm is used to set all pixels with an intensity greater than 128 to 1
and the rest to 0.
Then the SeparateObjects algorithm is applied to disconnect the connected particles. This method computes a watershed on the distance map to detect isthmuses joining adjacent particles.
Many particles are touching the border of the image field. Since their entire shapes are unknown, these objects would generate a bias when measuring individual features on the particles. Therefore, the BorderKill algorithm is used to remove these objects.
Last, a labelization step is performed to assign a unique value to each set of connected pixels. In this way all particles are identified.
Figure 1. Particle segmentation (a) the initial image, (b) the thresholding result,
(c) watershed based separation and (d) final image after rejecting border objects and labelization
Once this segmentation phase is done, the analysis algorithm is launched after having selected four measurements to compute:
Note:
More than 250 other measurements are also available and described in the Native Measurements section of the ImageDev Reference Guide.
See also
Then the SeparateObjects algorithm is applied to disconnect the connected particles. This method computes a watershed on the distance map to detect isthmuses joining adjacent particles.
Many particles are touching the border of the image field. Since their entire shapes are unknown, these objects would generate a bias when measuring individual features on the particles. Therefore, the BorderKill algorithm is used to remove these objects.
Last, a labelization step is performed to assign a unique value to each set of connected pixels. In this way all particles are identified.
 (a) |
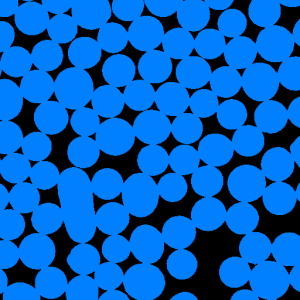 (b) |
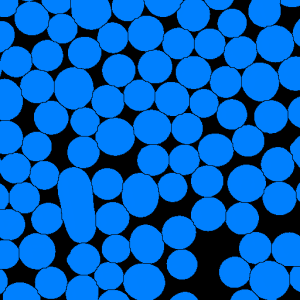 (c) |
 (d) |
Once this segmentation phase is done, the analysis algorithm is launched after having selected four measurements to compute:
- The X and Y center positions of the particles (the origin is the image top-left corner).
- The equivalent diameter of the particles (that is, the diameter of disks of same area).
- Their mean intensity in the original image.
| Number of particles = 58 | ||||
| Particle | BarycenterX | BarycenterY | EquivalentDiameter | IntensityMean |
| 1 | 395.75 | 39.01 | 49.46 | 206.28 |
| 2 | 105.89 | 48.58 | 50.75 | 225.12 |
| 3 | 248.53 | 56.56 | 61.04 | 227.68 |
| 4 | 192.00 | 63.94 | 52.13 | 212.79 |
| 5 | 469.05 | 74.31 | 63.93 | 229.77 |
Note:
More than 250 other measurements are also available and described in the Native Measurements section of the ImageDev Reference Guide.
#include <ImageDev/Data/AnalysisMsr.h>
#include <ImageDev/Data/NativeMeasurements.h>
#include <ImageDev/ImageDev.h>
#include <ioformat/IOFormat.h>
#include <iolink/view/ImageViewProvider.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace imagedev;
using namespace ioformat;
using namespace iolink;
int
main( int argc, char* argv[] )
{
int status = 0;
try
{
// ImageDev library initialization
if ( imagedev::isInitialized() == false )
imagedev::init();
// Open a standard tif file and display the image properties
auto imageInput = readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" );
// Threshold the grayscale image
auto imageThr =
thresholdingByCriterion( imageInput, ThresholdingByCriterion::ComparisonCriterion::GREATER_THAN, 128 );
// Separate connected particles
auto imageSep = separateObjects( imageThr,
2,
SeparateObjects::OutputType::SEPARATED_OBJECTS,
SeparateObjects::AlgorithmMode::REPEATABLE,
SeparateObjects::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 );
imageThr.reset();
// Remove particles touching image borders
auto imageBdk = borderKill( imageSep, BorderKill::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_26 );
imageSep.reset();
// Connected component labeling of a binary image
auto imageLab =
labeling2d( imageBdk, Labeling2d::LabelType::LABEL_8_BIT, Labeling2d::Neighborhood::CONNECTIVITY_8 );
// The number of particles is the maximum label
auto extrema = intensityExtrema( imageLab, 0 );
int particleCount = ( int )extrema->maximum( 0, 0, 0 );
// Define the analysis features to be computed
AnalysisMsr::Ptr analysis = std::make_shared< AnalysisMsr >();
auto centerX = analysis->select( NativeMeasurements::barycenterX );
auto centerY = analysis->select( NativeMeasurements::barycenterY );
auto diameter = analysis->select( NativeMeasurements::equivalentDiameter );
auto intensity = analysis->select( NativeMeasurements::intensityMean );
// Launch the feature extraction on the segmented image
labelAnalysis( imageLab, imageInput, analysis );
std::cout << "Number of particles = " << particleCount << std::endl;
std::cout << "Particle\t" << centerX->name() << "\t" << centerY->name() << "\t"
<< diameter->name() + "\t" + intensity->name() << std::endl;
// Print the analysis results for 10% of the particles
for ( int i = 0; i < ( int )( particleCount / 10 ); i++ )
{
std::cout << ( i + 1 ) << "\t\t" << centerX->value( i ) << "\t\t" << centerY->value( i ) << "\t\t"
<< diameter->value( i ) << "\t\t\t" << intensity->value( i ) << std::endl;
}
// Save the created image with IOFormat
writeView( imageLab, "T06_01_output.png" );
std::cout << "This example ran successfully." << std::endl;
}
catch ( const imagedev::Exception& error )
{
// Print potential exception in the standard output
std::cerr << "ImageDev exception: " << error.what() << std::endl;
status = -1;
}
// ImageDev library finalization
imagedev::finish();
// Check if we must ask for an enter key to close the program
if ( !( ( argc == 2 ) && strcmp( argv[1], "--no-stop-at-end" ) == 0 ) )
std::cout << "Press Enter key to close this window." << std::endl, getchar();
return status;
}
using System;
using ImageDev;
using IOLink;
using IOFormat;
namespace T06_01_ParticleAnalysis
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int status = 0;
try
{
// ImageDev library initialization
Initialization.Init();
// Open a standard tif file and display the image properties
ImageView imageInput = ViewIO.ReadImage("Data/images/polystyrene.tif");
// Threshold the grayscale image
ImageView imageThr = Processing.ThresholdingByCriterion(
imageInput, ThresholdingByCriterion.ComparisonCriterion.GREATER_THAN, 128);
// Separate connected particles
ImageView imageSep = Processing.SeparateObjects(imageThr, 2);
imageThr.Dispose();
// Remove particles touching image borders
ImageView imageBdk = Processing.BorderKill(imageSep);
imageSep.Dispose();
// Connected component labeling of a binary image
var imageLab = Processing.Labeling2d(imageBdk,
Labeling2d.LabelType.LABEL_8_BIT,
Labeling2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8);
// The number of particles is the maximum label
var extrema = Processing.IntensityExtrema(imageLab, 0) as IntensityExtremaMsr;
int particleCount = (int)extrema.maximum(0, 0, 0);
// Define the analysis features to be computed
AnalysisMsr analysis = new AnalysisMsr();
var centerX = analysis.Select(NativeMeasurements.BarycenterX);
var centerY = analysis.Select(NativeMeasurements.BarycenterY);
var diameter = analysis.Select(NativeMeasurements.EquivalentDiameter);
var intensity = analysis.Select(NativeMeasurements.IntensityMean);
// Launch the feature extraction on the segmented image
Processing.LabelAnalysis(imageLab, imageInput, analysis);
Console.WriteLine("Number of particles = " + particleCount);
Console.WriteLine("Particle\t" + centerX.Name() + "\t" + centerY.Name() + "\t" + diameter.Name() + "\t" +
intensity.Name());
// Print the analysis results for 10% of the particles
for (int i = 0; i < (int)(particleCount / 10); i++)
{
Console.WriteLine((i + 1) + "\t\t" + centerX.Value(i).ToString("0.00") + "\t\t" +
centerY.Value(i).ToString("0.00") + "\t\t" +
diameter.Value(i).ToString("0.00") + "\t\t\t" +
intensity.Value(i).ToString("0.00"));
}
// Save the created image with IOFormat
ViewIO.WriteView(imageBdk, "T06_01_output.png");
}
catch (Exception error)
{
// Print potential exception in the standard output
System.Console.WriteLine("HelloImageDev exception: " + error.ToString());
status = -1;
}
// ImageDev library finalization
Initialization.Finish();
// Check if we must ask for an enter key to close the program
if (!((args.Length >= 1) && (args[0] == "--no-stop-at-end")))
{
System.Console.WriteLine("Press Enter key to close this window.");
System.Console.ReadKey();
}
System.Environment.Exit(status);
}
}
}
import imagedev
import imagedev_data
import ioformat
# Initialize the ImageDev library if not done
if (imagedev.is_initialized() == False): imagedev.init()
# Open and display a tif file
image_input = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
# Threshold the grayscale image
image_thr = imagedev.thresholding_by_criterion(\
image_input, imagedev.ThresholdingByCriterion.ComparisonCriterion.GREATER_THAN, 128)
# Separate connected particles
image_sep = imagedev.separate_objects(image_thr, 2)
image_thr = None
# Remove particles touching image borders
image_bdk = imagedev.border_kill(image_sep)
image_sep = None
# Connected component labeling of a binary image
image_lab = imagedev.labeling_2d(\
image_bdk, imagedev.Labeling2d.LabelType.LABEL_8_BIT, imagedev.Labeling2d.Neighborhood.CONNECTIVITY_8)
# The number of particles is the maximum label
extrema = imagedev.intensity_extrema(image_lab, 0)
particle_count = int(extrema.maximum(0, 0, 0))
# Define the analysis features to be computed
analysis = imagedev.AnalysisMsr()
center_x = analysis.select(imagedev.native_measurements.BarycenterX)
center_y = analysis.select(imagedev.native_measurements.BarycenterY)
diameter = analysis.select(imagedev.native_measurements.EquivalentDiameter)
intensity = analysis.select(imagedev.native_measurements.IntensityMean)
# Launch the feature extraction on the segmented image
imagedev.label_analysis(image_lab, image_input, analysis)
print("Number of particles = " + str(particle_count))
print("Particle\t" + center_x.name + "\t" + center_y.name + "\t" + diameter.name + "\t" + intensity.name)
# Print the analysis results for 10% of the particles
for i in range(int(particle_count/10)):
print(str(i+1) + '\t\t\t' + "{:.2f}".format(center_x.value(i)) +'\t\t' + "{:.2f}".format(center_y.value(i)) +\
'\t\t' + "{:.2f}".format(diameter.value(i)) + '\t\t\t\t' + "{:.2f}".format(intensity.value(i)))
# Save the created image with IOFormat
ioformat.write_view(image_lab, "T06_01_output.png")
# ImageDev library finalization
imagedev.finish() See also