CrossCorrelation2d
Performs a correlation by convolution between a two-dimensional grayscale image and a grayscale kernel.
Access to parameter description
For an introduction: section Image Correlation.
This algorithm performs a cross-correlation, or correlation with a mutiplication metric, between a gray level image $I$ and a gray level kernel $K$, returning the correlation image $O$.
The different possibilities for selecting a correlation peak are presented below using a 1-D correlation between an image and kernel. In the image, the kernel appears 6 times with different contrast and luminosity.
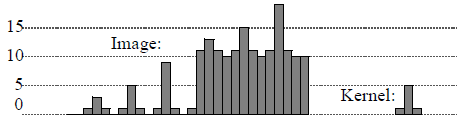
Figure 1. 1D image and kernel
The 6 examples show the kernel appearing with different contrast and luminosity.
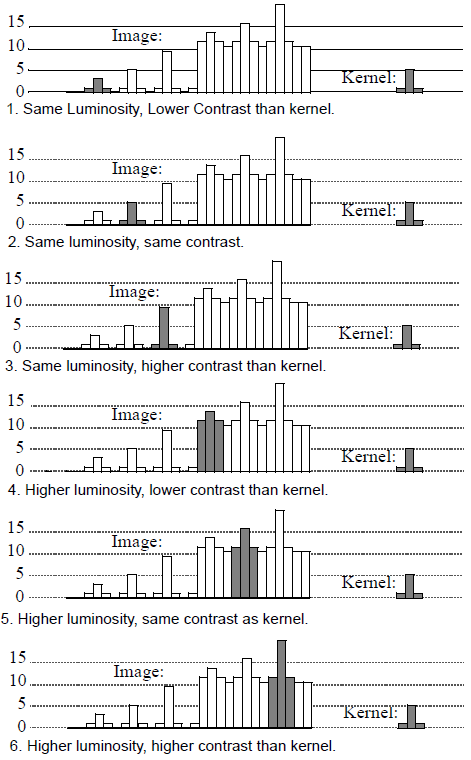
Figure 2. Examples of possible 1D correlation
The cross-correlation metric is computed in accordance with the CorrelationMode parameter.
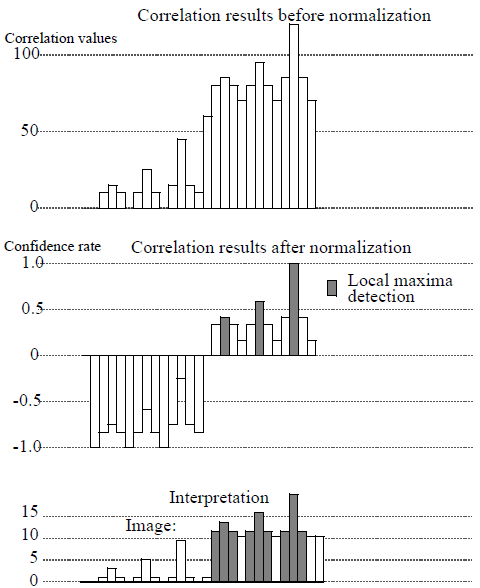
Figure 3. Example of 1D direct cross-correlation
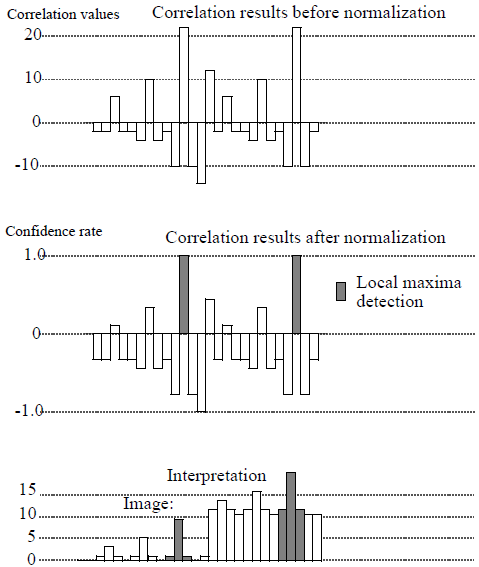
Figure 4. Example of 1D mean cross-correlation
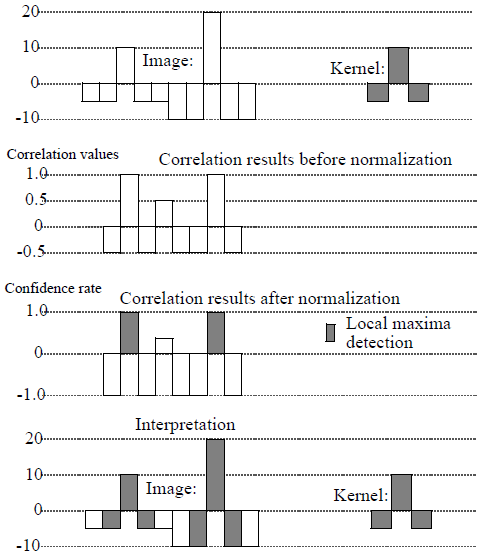
Figure 5. Example of 1D variance cross-correlation
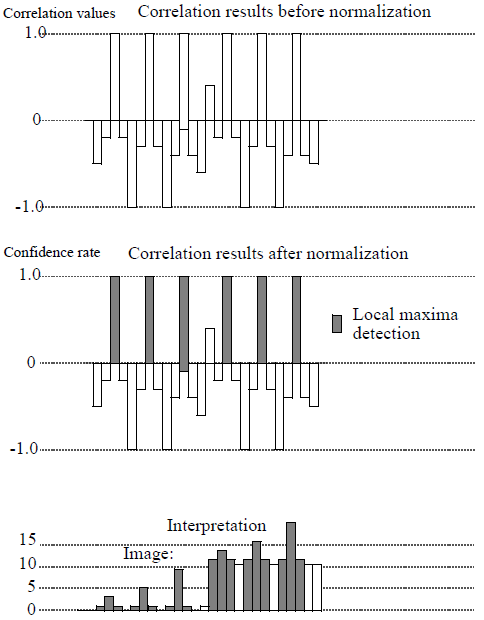
Figure 6: Example of 1D mean and variance cross-correlation
where: $$ \mu(K)=\frac{\sum\limits_{i=1}^{kx} \sum\limits_{j=1}^{ky} K(i,j)}{kx\times ky} $$ $$ \mu(I)(n,m)=\frac{\sum\limits_{i=1}^{kx} \sum\limits_{j=1}^{ky} I(n+i,m+j)}{kx\times ky} $$ $$ \sigma^2(K)=\sum_{i=1}^{kx} \sum_{j=1}^{ky} \left(K(i,j)-\mu(K)\right)^{2} $$ $$ \sigma^2(I)(n,m)=\sum_{i=1}^{kx} \sum_{j=1}^{ky} \left( I(n+i-\frac{kx}{2},m+j-\frac{ky}{2} ) - \mu(I)(n,m)\right)^{2} $$
Note: This algorithm returns the main correlation peak in the outputMeasurement object. More correlation peaks can be extracted from the outputImage correlation image with the LocalMaxima2d algorithm
See also
Access to parameter description
For an introduction: section Image Correlation.
This algorithm performs a cross-correlation, or correlation with a mutiplication metric, between a gray level image $I$ and a gray level kernel $K$, returning the correlation image $O$.
The different possibilities for selecting a correlation peak are presented below using a 1-D correlation between an image and kernel. In the image, the kernel appears 6 times with different contrast and luminosity.

Figure 1. 1D image and kernel
The 6 examples show the kernel appearing with different contrast and luminosity.

Figure 2. Examples of possible 1D correlation
The cross-correlation metric is computed in accordance with the CorrelationMode parameter.
DIRECT Correlation Mode
$$ O(n,m)=\sum_{i=1}^{kx} \sum_{j=1}^{ky} K(i,j)\times I\left(n+i-\frac{kx}{2},m+j-\frac{ky}{2}\right) $$ In this mode, 3 of the 6 patterns matching the kernel are detected. These are only high luminosity patterns. The best matching is obtained for the highest contrast and luminosity pattern.
Figure 3. Example of 1D direct cross-correlation
MEAN Correlation Mode
$$ O(n,m)=\sum_{i=1}^{kx} \sum_{j=1}^{ky} \left(K(i,j)-\mu(K)\right)\times \left(I(n+i-\frac{kx}{2},m+j-\frac{ky}{2})-\mu(I)(n,m)\right) $$ In this mode, 2 of the 6 patterns matching the kernel are detected. These are only high contrast patterns. The confidence rate is the same for the two 2 patterns.
Figure 4. Example of 1D mean cross-correlation
VARIANCE Correlation Mode
$$ O(n,m)=\frac{\sum\limits_{i=1}^{kx} \sum\limits_{j=1}^{ky} K(i,j)\times I(n+i-\frac{kx}{2},m+j- \frac{ky}{2})}{\sqrt{\sigma^2(K)\times \sigma^2(I)(n,m)}} $$ In this mode, 2 patterns matching the kernel are detected, with the same confidence rate.
Figure 5. Example of 1D variance cross-correlation
MEAN_VARIANCE Correlation Mode
$$ O(n,m)=\frac{\sum\limits_{i=1}^{kx} \sum\limits_{j=1}^{ky} \left(K(i,j)-\mu(K)\right)\times \left(I(n+i-\frac{kx}{2},m+j-\frac{ky}{2})-\mu(I)(n,m)\right)}{\sqrt{\sigma^2(K)\times \sigma^2(I)(n,m)}} $$ In this mode, the 6 patterns matching the kernel are detected, with the same confidence rate.
Figure 6: Example of 1D mean and variance cross-correlation
where: $$ \mu(K)=\frac{\sum\limits_{i=1}^{kx} \sum\limits_{j=1}^{ky} K(i,j)}{kx\times ky} $$ $$ \mu(I)(n,m)=\frac{\sum\limits_{i=1}^{kx} \sum\limits_{j=1}^{ky} I(n+i,m+j)}{kx\times ky} $$ $$ \sigma^2(K)=\sum_{i=1}^{kx} \sum_{j=1}^{ky} \left(K(i,j)-\mu(K)\right)^{2} $$ $$ \sigma^2(I)(n,m)=\sum_{i=1}^{kx} \sum_{j=1}^{ky} \left( I(n+i-\frac{kx}{2},m+j-\frac{ky}{2} ) - \mu(I)(n,m)\right)^{2} $$
Note: This algorithm returns the main correlation peak in the outputMeasurement object. More correlation peaks can be extracted from the outputImage correlation image with the LocalMaxima2d algorithm
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns a CrossCorrelation2dOutput structure containing outputImage and outputMeasurement.
// Output structure of the crossCorrelation2d function.
struct CrossCorrelation2dOutput
{
/// The output correlation image. Its dimensions are forced to the same values as the input. Its data type is forced to floating point.
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage;
/// The correlation matching results.
CrossCorrelation2dMsr::Ptr outputMeasurement;
};
// Function prototype
CrossCorrelation2dOutput
crossCorrelation2d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputKernelImage,
CrossCorrelation2d::CorrelationMode correlationMode,
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = NULL,
CrossCorrelation2dMsr::Ptr outputMeasurement = NULL );
This function returns a tuple containing output_image and output_measurement.
// Function prototype.
cross_correlation_2d( input_image,
input_kernel_image,
correlation_mode = CrossCorrelation2d.CorrelationMode.DIRECT,
output_image = None,
output_measurement = None )
This function returns a CrossCorrelation2dOutput structure containing outputImage and outputMeasurement.
/// Output structure of the CrossCorrelation2d function.
public struct CrossCorrelation2dOutput
{
///
/// The output correlation image. Its dimensions are forced to the same values as the input. Its data type is forced to floating point.
///
public IOLink.ImageView outputImage;
/// The correlation matching results.
public CrossCorrelation2dMsr outputMeasurement;
};
// Function prototype.
public static CrossCorrelation2dOutput
CrossCorrelation2d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
IOLink.ImageView inputKernelImage,
CrossCorrelation2d.CorrelationMode correlationMode = ImageDev.CrossCorrelation2d.CorrelationMode.DIRECT,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null,
CrossCorrelation2dMsr outputMeasurement = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Class Name | CrossCorrelation2d |
|---|
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input grayscale image. | Image | Grayscale | nullptr | ||||||||
 |
inputKernelImage |
The correlation kernel. | Image | Grayscale | nullptr | ||||||||
 |
correlationMode |
The normalization mode for correlation.
|
Enumeration | DIRECT | |||||||||
 |
outputImage |
The output correlation image. Its dimensions are forced to the same values as the input. Its data type is forced to floating point. | Image | nullptr | |||||||||
 |
outputMeasurement |
The correlation matching results. | CrossCorrelation2dMsr | nullptr | |||||||||
Object Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); CrossCorrelation2d crossCorrelation2dAlgo; crossCorrelation2dAlgo.setInputImage( polystyrene ); crossCorrelation2dAlgo.setInputKernelImage( polystyrene ); crossCorrelation2dAlgo.setCorrelationMode( CrossCorrelation2d::CorrelationMode::DIRECT ); crossCorrelation2dAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputImage:" << crossCorrelation2dAlgo.outputImage()->toString(); std::cout << "matchingPositionX: " << crossCorrelation2dAlgo.outputMeasurement()->matchingPositionX( 0 ) ;
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
cross_correlation_2d_algo = imagedev.CrossCorrelation2d()
cross_correlation_2d_algo.input_image = polystyrene
cross_correlation_2d_algo.input_kernel_image = polystyrene
cross_correlation_2d_algo.correlation_mode = imagedev.CrossCorrelation2d.DIRECT
cross_correlation_2d_algo.execute()
print( "output_image:", str( cross_correlation_2d_algo.output_image ) )
print( "matchingPositionX: ", str( cross_correlation_2d_algo.output_measurement.matching_position_x( 0 ) ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" );
CrossCorrelation2d crossCorrelation2dAlgo = new CrossCorrelation2d
{
inputImage = polystyrene,
inputKernelImage = polystyrene,
correlationMode = CrossCorrelation2d.CorrelationMode.DIRECT
};
crossCorrelation2dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + crossCorrelation2dAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine( "matchingPositionX: " + crossCorrelation2dAlgo.outputMeasurement.matchingPositionX( 0 ) );
Function Examples
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > polystyrene = ioformat::readImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "polystyrene.tif" ); auto result = crossCorrelation2d( polystyrene, polystyrene, CrossCorrelation2d::CorrelationMode::DIRECT ); std::cout << "outputImage:" << result.outputImage->toString(); std::cout << "matchingPositionX: " << result.outputMeasurement->matchingPositionX( 0 ) ;
polystyrene = ioformat.read_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("polystyrene.tif"))
result_output_image, result_output_measurement = imagedev.cross_correlation_2d( polystyrene, polystyrene, imagedev.CrossCorrelation2d.DIRECT )
print( "output_image:", str( result_output_image ) )
print( "matchingPositionX: ", str( result_output_measurement.matching_position_x( 0 ) ) )
ImageView polystyrene = ViewIO.ReadImage( @"Data/images/polystyrene.tif" ); Processing.CrossCorrelation2dOutput result = Processing.CrossCorrelation2d( polystyrene, polystyrene, CrossCorrelation2d.CorrelationMode.DIRECT ); Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.outputImage.ToString() ); Console.WriteLine( "matchingPositionX: " + result.outputMeasurement.matchingPositionX( 0 ) );