ClosingLine3d
Performs a three-dimensional closing using a structuring element matching with a line.
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
The dilation line is oriented in the direction given by ($\theta$, $\varphi$) in spherical coordinates as often used in mathematics (azimuthal angle, $\theta$ and polar angle, $\varphi$). This direction is described with the following formula: $$V=\left[\begin{array}{c}; v_x\\ v_y\\ v_z\end{array}\right] = \left[\begin{array}{c}; \sin(\varphi)\cos(\theta)\\ \sin(\varphi)\sin(\theta)\\ \cos(\varphi)\end{array}\right]$$ This direction can be illustrated on the unit sphere:
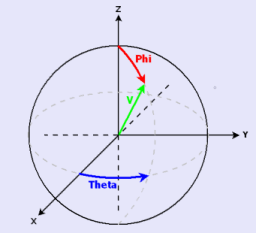
Figure 1. Azimuthal and polar angles on the unit sphere
With a classic implementation, morphological closing systematically considers areas out of the image as a replication of the image borders at each step of the algorithm. Therefore, when applying a closing, some objects close to the image borders may be connected to the border at the dilation step and not be retro propagated after the dilation, while one would expect to keep them disconnected from the border. The borderPolicy parameter manages this case. The default mode, LIMITED, corresponds to the classic behavior. The EXTENDED mode properly manages image borders by extending them by a size equal to the structuring element's. This mode can be slower and more memory consuming, especially when the structuring element size is high.
This option is illustrated in the Closing2d documentation (Figure 2).
See also
Access to parameter description
For an introduction:
- section Mathematical Morphology
- section Introduction To Closing
The dilation line is oriented in the direction given by ($\theta$, $\varphi$) in spherical coordinates as often used in mathematics (azimuthal angle, $\theta$ and polar angle, $\varphi$). This direction is described with the following formula: $$V=\left[\begin{array}{c}; v_x\\ v_y\\ v_z\end{array}\right] = \left[\begin{array}{c}; \sin(\varphi)\cos(\theta)\\ \sin(\varphi)\sin(\theta)\\ \cos(\varphi)\end{array}\right]$$ This direction can be illustrated on the unit sphere:

Figure 1. Azimuthal and polar angles on the unit sphere
With a classic implementation, morphological closing systematically considers areas out of the image as a replication of the image borders at each step of the algorithm. Therefore, when applying a closing, some objects close to the image borders may be connected to the border at the dilation step and not be retro propagated after the dilation, while one would expect to keep them disconnected from the border. The borderPolicy parameter manages this case. The default mode, LIMITED, corresponds to the classic behavior. The EXTENDED mode properly manages image borders by extending them by a size equal to the structuring element's. This mode can be slower and more memory consuming, especially when the structuring element size is high.
This option is illustrated in the Closing2d documentation (Figure 2).
See also
Function Syntax
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype
std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > closingLine3d( std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > inputImage, double thetaAngle, double phiAngle, uint32_t kernelRadius, ClosingLine3d::BorderPolicy borderPolicy, std::shared_ptr< iolink::ImageView > outputImage = NULL );
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype.
closing_line_3d( input_image,
theta_angle = 0,
phi_angle = 0,
kernel_radius = 3,
border_policy = ClosingLine3d.BorderPolicy.LIMITED,
output_image = None )
This function returns outputImage.
// Function prototype.
public static IOLink.ImageView
ClosingLine3d( IOLink.ImageView inputImage,
double thetaAngle = 0,
double phiAngle = 0,
UInt32 kernelRadius = 3,
ClosingLine3d.BorderPolicy borderPolicy = ImageDev.ClosingLine3d.BorderPolicy.LIMITED,
IOLink.ImageView outputImage = null );
Class Syntax
Parameters
| Class Name | ClosingLine3d |
|---|
| Parameter Name | Description | Type | Supported Values | Default Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inputImage |
The input image. The image type can be integer or float. | Image | Binary, Label, Grayscale or Multispectral | nullptr | ||||
 |
borderPolicy |
The border policy to apply.
|
Enumeration | LIMITED | |||||
 |
thetaAngle |
The azimuthal angle in degrees. | Float64 | Any value | 0 | ||||
 |
phiAngle |
The polar angle in degrees. | Float64 | Any value | 0 | ||||
 |
kernelRadius |
The length of the linear structuring element in voxels. | UInt32 | >=1 | 3 | ||||
 |
outputImage |
The output image. Its dimensions and type are forced to the same values as the input image. | Image | nullptr | |||||
Object Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); ClosingLine3d closingLine3dAlgo; closingLine3dAlgo.setInputImage( foam ); closingLine3dAlgo.setThetaAngle( 0 ); closingLine3dAlgo.setPhiAngle( 0 ); closingLine3dAlgo.setKernelRadius( 3 ); closingLine3dAlgo.setBorderPolicy( ClosingLine3d::BorderPolicy::EXTENDED ); closingLine3dAlgo.execute(); std::cout << "outputImage:" << closingLine3dAlgo.outputImage()->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
closing_line_3d_algo = imagedev.ClosingLine3d()
closing_line_3d_algo.input_image = foam
closing_line_3d_algo.theta_angle = 0
closing_line_3d_algo.phi_angle = 0
closing_line_3d_algo.kernel_radius = 3
closing_line_3d_algo.border_policy = imagedev.ClosingLine3d.EXTENDED
closing_line_3d_algo.execute()
print( "output_image:", str( closing_line_3d_algo.output_image ) )
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" );
ClosingLine3d closingLine3dAlgo = new ClosingLine3d
{
inputImage = foam,
thetaAngle = 0,
phiAngle = 0,
kernelRadius = 3,
borderPolicy = ClosingLine3d.BorderPolicy.EXTENDED
};
closingLine3dAlgo.Execute();
Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + closingLine3dAlgo.outputImage.ToString() );
Function Examples
auto foam = readVipImage( std::string( IMAGEDEVDATA_IMAGES_FOLDER ) + "foam.vip" ); auto result = closingLine3d( foam, 0, 0, 3, ClosingLine3d::BorderPolicy::EXTENDED ); std::cout << "outputImage:" << result->toString();
foam = imagedev.read_vip_image(imagedev_data.get_image_path("foam.vip"))
result = imagedev.closing_line_3d( foam, 0, 0, 3, imagedev.ClosingLine3d.EXTENDED )
print( "output_image:", str( result ) )
ImageView foam = Data.ReadVipImage( @"Data/images/foam.vip" ); IOLink.ImageView result = Processing.ClosingLine3d( foam, 0, 0, 3, ClosingLine3d.BorderPolicy.EXTENDED ); Console.WriteLine( "outputImage:" + result.ToString() );